
Credit score: Dominick Reuter/AFP through Getty
For somewhat greater than a century, chemists have believed that robust atomic hyperlinks known as covalent bonds are fashioned when atoms share a number of electron pairs. Now, researchers have made the primary observations of single-electron covalent bonds between two carbon atoms.
This uncommon bonding behaviour has been seen between a number of different atoms, however scientists are notably excited to see it in carbon, the essential constructing block of life on Earth and the important thing part of commercial chemical substances together with medicine, plastics, sugars and proteins. The invention was printed1 in Nature on 25 September.
“The covalent bond is without doubt one of the most vital ideas in chemistry, and discovery of recent kinds of chemical bonds holds nice promise for increasing huge areas of chemical area,” says College of Tokyo chemist Takuya Shimajiri, who was a part of the carbon bonding analysis crew.
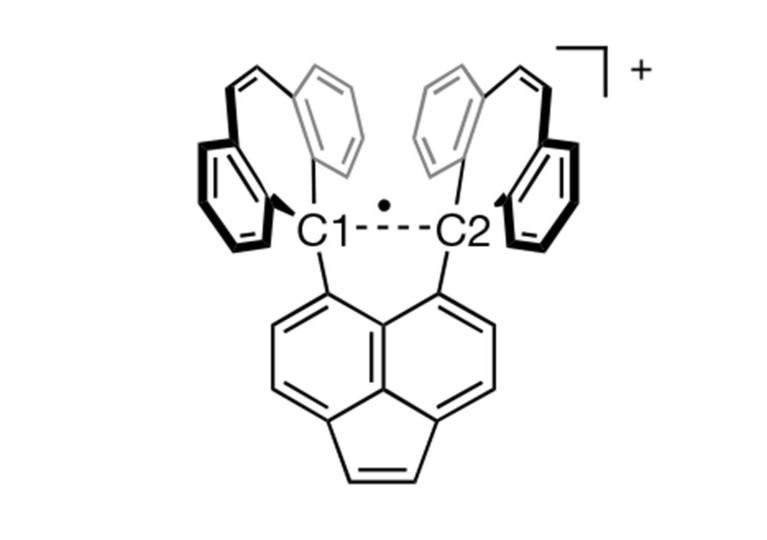
Credit score: Takuya Shimajiri et al./Nature
Most chemical bonds in molecules are made up of a single pair of electrons, shared between atoms. These are known as covalent single bonds. In notably robust bonds, atoms may share two electron pairs in a double bond, or three pairs — a triple bond. However chemists know that atoms work together in lots of different methods, and by finding out extra uncommon bond varieties on the boundaries of the doable, they hope to higher perceive what a chemical bond is within the first place.
Pauling’s proposal
The idea of single-electron covalent bonds dates to 1931, when chemist Linus Pauling proposed them. However on the time, chemists didn’t have the instruments to watch such bonds, says Marc-Etienne Moret, a chemist at Utrecht College within the Netherlands. Even with trendy analytical strategies, these bonds are difficult to watch. “The state of affairs during which just one electron makes a bond may be very unstable,” says Moret. “This implies the bond will break simply and have a powerful tendency to both launch or seize an electron to revive a good variety of electrons.”
In 1998, scientists noticed2 a single-electron bond between two phosphorus atoms; Moret was a part of a bunch that created3 one between copper and boron in 2013. Chemists have theorized that these uncommon bonds may happen between carbon atoms in short-lived intermediate constructions that seem throughout chemical reactions. However to watch these fickle bonds, chemists should stabilize a compound that incorporates them. A steady compound that incorporates a one-electron C–C bond had eluded chemists.
Shimajiri says the important thing to observing the single-electron carbon bond was rigorously designing a molecule that might stabilize it. The analysis crew, which included Hokkaido College chemist Yusuke Ishigaki, created a molecule that gives a steady ‘shell’ of fused carbon rings that helps maintain collectively the carbon–carbon bond in its centre. That central bond is stretched out to a comparatively lengthy size for a C–C bond, which makes it prone to dropping one electron in an oxidation response, creating the elusive single-electron bond.
Uncommon oxygen isotope detected eventually — and it defies expectations
Secure bond
To seize this compound in a steady, observable kind, they crystallized it. When the oxidation is carried out within the presence of iodine, the response yields a purple salt, with the steady shell of the molecule holding collectively the single-electron C–C bond inside. They then used numerous analytical strategies to characterize the molecule and the bond. Shimajiri says the compound is extraordinarily steady underneath ambient circumstances.
“In a number of chemical reactions, the involvement of one-electron bonds has been proposed, however thus far, they’ve remained hypothetical,” says Shimajiri. Creating steady compounds containing these bonds might assist researchers to higher perceive what occurs throughout these reactions.
Man Bertrand, a chemist on the College of California, Santa Barbara, was a part of the crew that created the phosphorus single-electron bond. He says it’s important to see it in carbon. “Anytime you do one thing with carbon, the influence is bigger than with another factor,” he says. Carbon is the stuff of natural chemistry. However he says it’s not really easy to say whether or not this work can have any functions. “This can be a curiosity,” he says. “However it is going to be within the textbooks.”
Shimajiri hopes that the outline of the single-electron carbon bond will assist chemists to higher perceive the essential nature of chemical bonds. “We goal to make clear what a covalent bond is — particularly, at what level does a bond qualify as covalent, and at what level does it not?”



