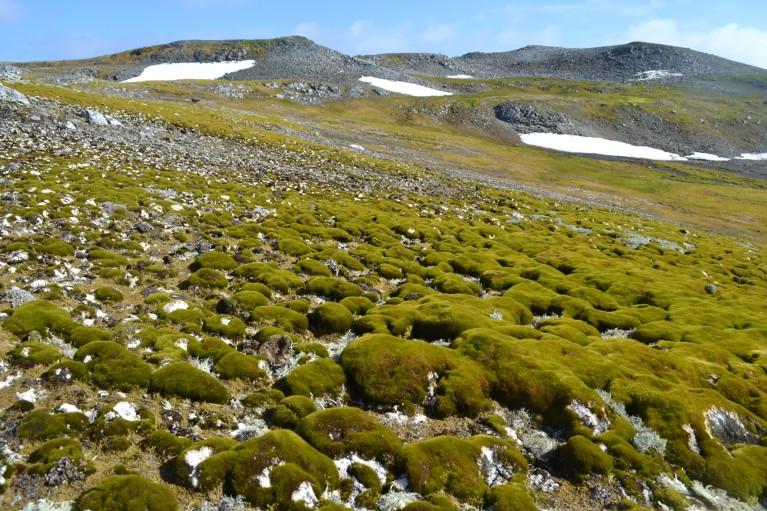

Hummocks of moss cowl Ardley Island off the tip of the Antarctic Peninsula.Credit score: Dan Charman
A fast-warming area of Antarctica is getting greener with stunning velocity. Satellite tv for pc imagery of the area reveals that the realm coated by vegetation elevated by nearly 14 occasions over 35 years — a development that may spur speedy change of Antarctic ecosystems.
“It is the start of dramatic transformation,” says Olly Bartlett, a remote-sensing specialist on the College of Hertfordshire in Hatfield, UK, and an creator of the research1, printed right this moment in Nature Geoscience, that studies these outcomes.
From white to inexperienced
Bartlett and his colleagues analysed pictures taken between 1986 and 2021 of the Antarctic Peninsula — part of the continent that juts north in direction of the tip of South America. The images had been taken by the Landsat satellites operated by NASA and the US Geological Survey in March, which is the top of the rising season for vegetation within the Antarctic.
To evaluate how a lot of the land was coated with vegetation, the researchers took benefit of the properties of rising vegetation: wholesome vegetation take in numerous crimson mild and replicate numerous near-infrared mild. Scientists can use satellite tv for pc measurements of sunshine at these wavelengths to find out whether or not a bit of land is roofed by thriving vegetation.
The staff discovered that the realm of the peninsula swathed in vegetation grew from lower than one sq. kilometre in 1986 to just about 12 sq. kilometres in 2021 (see ‘An icy land goes inexperienced’). The speed of growth was roughly 33% increased between 2016 and 2021 in contrast with the four-decade research interval as a complete.
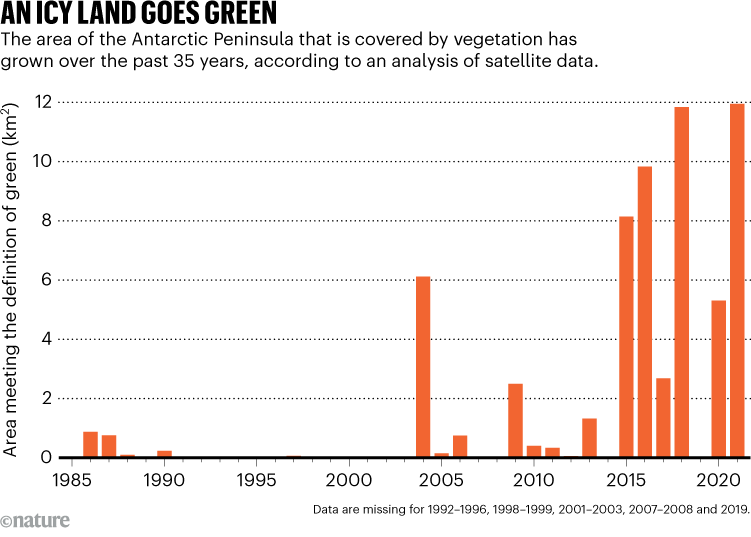
Supply: Ref. 1
“These numbers shocked us,” says Thomas Roland, a research co-author and an environmental scientist on the College of Exeter, UK. “It is merely that fee of change in an especially remoted, extraordinarily weak space that causes the alarm.”
The analysis is “actually necessary”, says Jasmine Lee, a conservation scientist on the British Antarctic Survey in Cambridge, UK. Different research2,3 have discovered proof that vegetation on the peninsula is altering in response to local weather change, “however that is the primary research that is taken a huge-scale strategy to have a look at the complete area”, she says.
Earlier visits by the authors to the peninsula lead the authors to assume that many of the vegetation is moss. As mosses unfold to beforehand ice-covered landscapes, they may construct up a layer of soil, providing a habitat for different vegetation, Roland says. “There’s an enormous potential right here to see an extra improve within the quantity of non-native, probably invasive species,” he says.
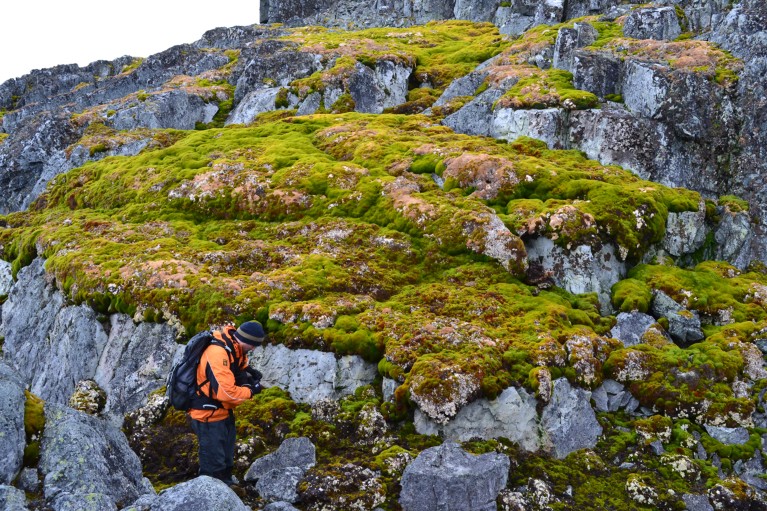

Moss covers rocks on Norsel Level, an arm of an island off the Antarctic Peninsula.Credit score: Dan Charman
It is a concern as a result of Antarctica’s native flora are tailored to excessive circumstances, and they may not be capable of compete with an inflow of different species, Lee says.
The researchers level to local weather change as the driving force of the panorama’s shift from white to inexperienced. Temperatures on the peninsula have risen by nearly 3°C since 1950, which is a a lot greater improve than noticed throughout most components of the planet. The “phenomenal” fee of growth of greenery, Roland says, highlights the unprecedented adjustments that people are imposing on Earth’s local weather.


