Wildfires have existed for so long as crops have been on land. These fires usually are not inherently dangerous, however in lots of areas they’re changing into bigger, extra intense and faster-moving. Within the western United States, intensive fires at the moment are commonplace. For instance, in July, the Park wildfire in northern California unfold to greater than 50,000 hectares in its first 24 hours — the equal of round one soccer area per second. Over one month, it grew to burn 170,000 hectares, an space half the scale of Rhode Island. And the fireplace season may not be over but.
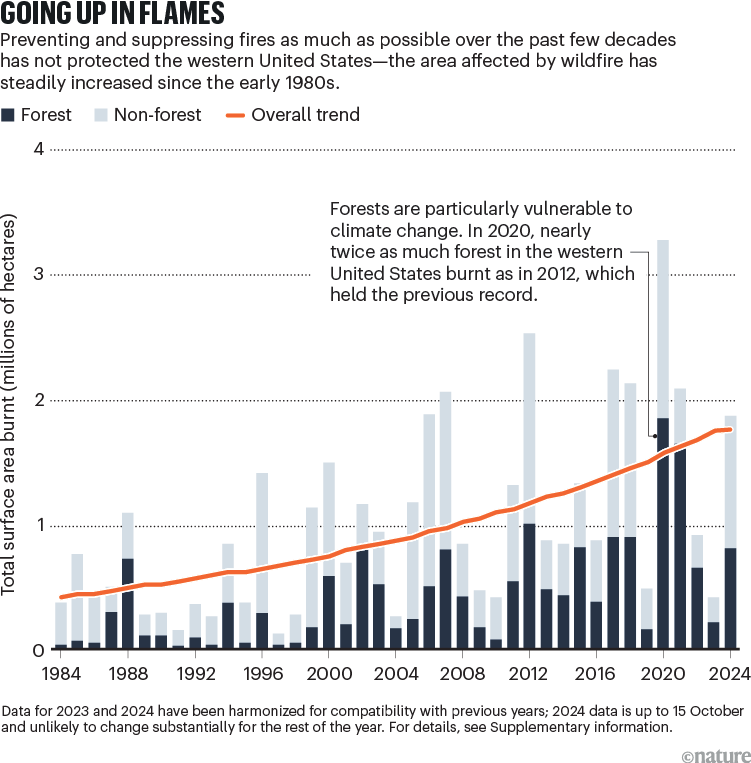
The realm of land burnt annually will increase exponentially with aridity1. And local weather change is making the fireplace season within the western United States each hotter and drier. The realm of forest that’s burnt in a yr is now ten instances what it was 4 many years in the past, aided partially by sooner charges of unfold, a examine printed as we speak exhibits2 (see ‘Going up in flames’). If, as anticipated, this area will get hotter and drier nonetheless, it’s possible that the file space burnt, forest and in any other case, in 2020 — 3.3 million hectares, bigger than Belgium — might be surpassed in 5–10 years. Folks and their houses will inevitably be within the path of a few of these occasions. America just isn’t ready.
See Supplementary Info
Up to now six years, simply three fast-moving wildfires — in Paradise, California, in 2018; the 2021 Marshall hearth in Colorado; and the 2023 hearth in Lahaina, Hawaii — destroyed hundreds of houses and collectively took greater than 150 lives. In addition to spreading flames and choking smoke, fires improve the likelihoods of water air pollution, flooding and mudslides by, for instance, killing vegetation that will in any other case regulate water run-off and stabilize soils.
Wildfires are spreading quick in Canada — we should strengthen forests for the longer term
A brand new method is required: folks should study to stay with wildfires. That was the conclusion of a 2023 report (see go.nature.com/415k8sc) by the Wildland Fireplace Mitigation and Administration Fee, created by the administration of US President Joe Biden in 2021 to advise on coverage to deal with the wildfire disaster. The report recognized three priorities: investing in expertise and knowledge evaluation to construct resilience to wildfires; shifting from an emergency response mode to a proactive mindset of fireside resilience; and cultivating useful types of hearth to take care of flammable lands.
Fireplace science wants a drastic shift, too3. Fashions should simulate complicated interactions between local weather, vegetation, wildfire and people on regional and international scales. Right here is the place the science should go over the following 5 years.
Embrace burning
When intense or quick wildfires can be unacceptable, they need to be both prevented from beginning or starved of gas. By ‘prescribed’ burning, rigorously managed fires can be utilized to skinny out fuels. And wildfires could be managed to realize an appropriate unfold, when climate circumstances or moisture ranges of their gas make it unlikely that they’ll change into speedy, high-intensity blazes4.
Indigenous information reveals historical past of fire-prone California forest
The idea of ‘good hearth’ has been a part of Conventional Ecological Data in North America for hundreds of years. Indigenous Peoples have lengthy carried out intentional burning for a lot of functions, together with decreasing gas density and selling the expansion of particular crops used for meals or supplies5. There’s nice potential for good hearth to be cultivated by Indigenous specialists and land managers. Impediments have to be eased, together with an absence of funding, challenges related to managing landscapes that unfold throughout a number of jurisdictions, and conflicts with environmental insurance policies such because the US Clear Air Act6.
But it surely’s usually onerous to steer the general public and politicians that fireplace could be useful. All fires trigger smoke, and even prescribed fires generally get uncontrolled, with catastrophic penalties. Over the previous century, the worry of such occasions has contributed to the US authorities’s deal with avoiding fires or suppressing them rapidly after they do get away. In consequence, many forests have change into filled with bushes and undergrowth, making them extra vulnerable to excessive fires.
Recognizing this danger, the US authorities has devoted billions of {dollars} to decreasing gas masses in forests, by prescribed hearth and different methods, as a part of its 2021 Infrastructure Funding and Jobs Act and its 2022 Inflation Discount Act (see go.nature.com/3y3xewk). However it’s unrealistic to cut back flamable supplies, and hold them diminished, throughout all vegetated landscapes of the western United States — the forested space of which is about 1.5 instances the scale of France.
Moreover, reductions in gas usually are not at all times useful to ecosystems. Species within the chaparral shrublands of California, for instance, and forests within the wettest mountain areas of the western United States have advanced to develop densely for many years or centuries till uncommon, sizzling fires reset the cycle. To prescribe fires too often or at too low an depth in these ecosystems would danger lack of native vegetation and the unfold of invasive grasses, facilitating extra fires7.
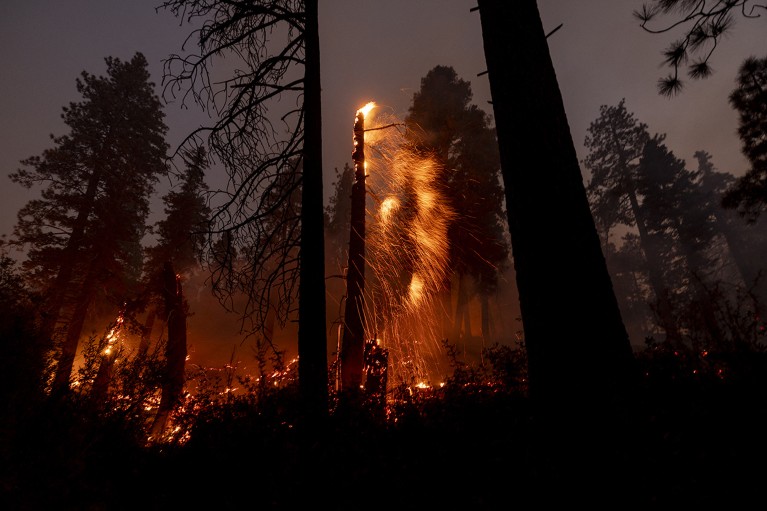

Dry and windy circumstances rendered the September Bridge hearth close to Wrightwood, California, ‘unpredictable’.Credit score: Etienne Laurent/AFP through Getty
To advise policymakers, researchers want to provide proof in regards to the trade-offs of intentional gas discount versus hearth suppression. For instance, a prescribed hearth comes at the price of smoke air pollution, but it surely additionally decreases the dangers of wildfires in an unnaturally dense forest throughout a record-setting heatwave.
Simulations of the possible outcomes of varied varieties of fires must be a part of this effort. The fashions want knowledge to tell them: correct maps of space burnt, development of unfold and hearth depth and severity for each wildfires and prescribed burns, in addition to vegetation traits equivalent to moisture content material and biomass construction, earlier than and lengthy after a hearth.
Put together for ecological change
In lots of locations, forests usually are not bouncing again after fires as they used to. Massive and extreme blazes can create gaps in forests which can be too giant for seeds to be unfold throughout8. Drought and warming may hinder tree regeneration. Though the boundaries of resilience are onerous to outline, many ecosystems are being pushed to thresholds at which they’re completely altered9.
Megafires are right here to remain — and blaming solely local weather change received’t assist
Forests harassed by altering circumstances want adaptive administration. This could take totally different varieties. In California’s Sierra Nevada mountains, for instance, the place some 15% of the world’s large sequoia bushes (Sequoiadendron giganteum) died in 2020 and 2021, it is perhaps price suppressing undesirable fires and planting sequoia seedlings with extra drought-resistant traits to keep away from additional losses10. However in different areas, longer-term interventions is perhaps extra applicable.
For instance, forest species which can be much less flammable, equivalent to aspen (Populus tremuloides), is perhaps planted to function pure limitations to speedy hearth unfold11. In hotter, drier areas within the southwestern United States, the place some forests have nonetheless not recovered years and even many years after extreme fires, it is perhaps clever for land managers to put money into reforesting with very heat-tolerant bushes, or to simply accept grass- and shrub-dominated ecosystems which can be tailored for intense, extended droughts and frequent fires.
Mannequin future fires
Fireplace and ecosystem modelling ought to inform responses to adjustments in wildfire exercise and assist to keep away from worst-case eventualities.
Earth-system fashions can approximate the overall character of vegetation distributions on the international scale. However these fashions are too coarse and easy to realistically simulate interactions between fires and ecosystems. To bridge this hole, researchers should construct on advances in intermediate-complexity modelling12, together with simulations of fireside–ecosystem dynamics throughout giant areas over timescales of many years to centuries.
As a result of there is no such thing as a single greatest method to modelling hearth for a given area, a number of modelling teams ought to be part of forces. The worldwide Fireplace Mannequin Intercomparison Challenge (see go.nature.com/3a4th9n) can function blueprint. On this initiative, researchers run totally different fashions utilizing a standardized set of information, examine their outputs and benchmark them in opposition to observations.
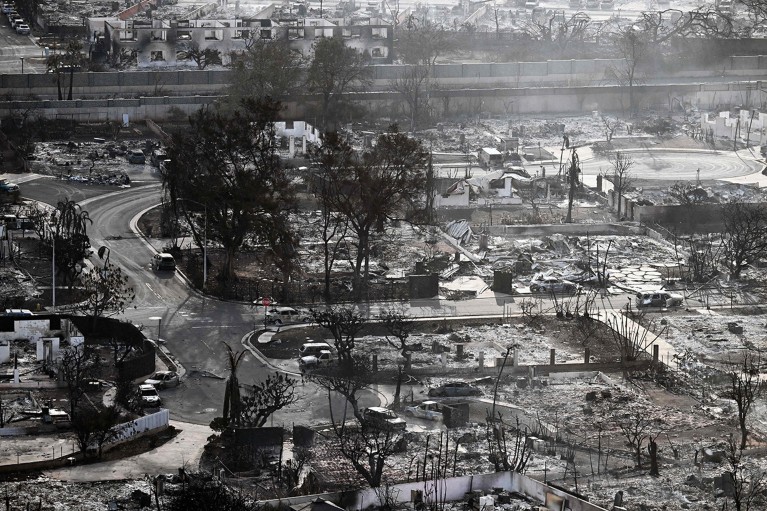

In 2023, a small hearth escaped containment and burnt by Lahaina, Hawaii, in simply 2 hours.Credit score: Patrick T. Fallon/AFP through Getty
The kind, abundance and water content material of vegetation have to be simulated. In stay vegetation, for instance, moisture content material relies on soils and roots, but additionally on particular person species’ methods to control water loss. The moisture ranges of grass and lifeless pine needles are very delicate to temperature. Extra-substantial fuels, equivalent to tree trunks, are slower to reply and might retain the impact of a drought or moist interval for months. To enhance the flexibility to simulate gas moisture dynamics, it’s crucial to proceed amassing, and enhancing, satellite tv for pc measurements of vegetation water content material13.
Are all of us doomed? How to deal with the daunting uncertainties of local weather change
Importantly, the understanding of future local weather is delicate to the flexibility to simulate future fires. Massive forest fires have been not too long ago proven to amplify warming domestically14, and hearth additionally influences local weather globally, in that vegetation shops carbon however releases it into the ambiance when burnt, largely as carbon dioxide and methane. It’s nonetheless unclear whether or not continental ecosystems will function sources or sinks for atmospheric carbon, and hearth will play an vital half in settling that subject. In California, the state’s formidable goal of carbon neutrality by 2045 (see go.nature.com/404c7sx) relies on the continued accumulation of carbon by its forested ecosystems — however more and more giant and extreme forest fires threaten this objective15.
Thus, higher regional hearth fashions are wanted to estimate future fires domestically, and higher international fashions are wanted to account for the impact of fires on the local weather. This implies enhancing the illustration of ecology in Earth-system fashions to higher perceive how several types of plant use water, whether or not crops die or survive on account of hearth and different disturbances, and the way ecosystems change over time.
Accumulate extra knowledge
Fireplace modelling is constrained by an absence of long-term observations of the incidence and extent of fires, in addition to their depth, smoke emissions and the consequences on ecosystems. Two or three many years of satellite tv for pc knowledge are sufficient to watch how hearth is distributed throughout the continents on common, however not sufficient to grasp the causes and results of change over time. Fires and their carbon emissions should proceed to be monitored globally, which might by no means be taken with no consideration given the brief lifespans of satellites.
On a regional stage, many governments hold data of fires — however these knowledge units are sometimes disparate, of questionable high quality, geographically inconsistent and incomplete. For instance, the US Forest Service has produced detailed satellite tv for pc maps of the extent and severity of hundreds of fires since 1984. However these maps characteristic solely the biggest 5% of fires, don’t embody info on how every hearth progressed, and cease on the US borders.
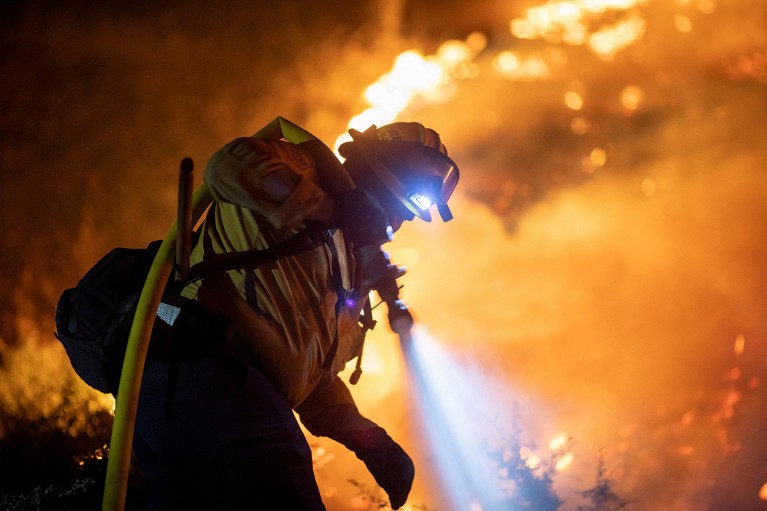

A firefighter tackles a blaze northeast of Los Angeles, California, in September 2024.Credit score: Ringo Chiu/Reuters
The US Forest Service additionally publishes a listing16 of two million US wildfires which have acquired suppression efforts since 1992, and their causes. But it surely lacks knowledge on the place precisely every hearth burnt, updates to the listing take years and reporting practices are inconsistent amongst authorities businesses. And these challenges are international. Actually, in contrast with many of the world, data of wildfires within the western United States are fairly good.
Complete archives, together with of satellite tv for pc imagery monitoring the unfold of particular person fires, have gotten accessible on-line. In the meantime, knowledge from sources equivalent to social media, in addition to housing data that seize property injury brought on by wildfires, must be made publicly accessible. Open-science ideas must be adopted for all hearth knowledge.
Reckon with human influences
Persons are usually the primary reason behind fires — however human behaviour is tough to foretell. It will have been not possible to foretell, for instance, that 4 July, US Independence Day, would change into the day with the best variety of wildfires in america.
Fires are managed otherwise in wildlands and in city zones: forests, shrubs and grasses want some fires, however populated areas don’t. The interface between these zones, the place flammable vegetation and human settlements intermingle, must be higher constructed to accommodate each.
The causes of wildfires are clear. How they burn by communities just isn’t
To raised simulate how hearth and ecosystems work together with people, and the way folks reply to rising hearth dangers, extra collaboration is required between bodily scientists, social scientists and economists. Authorities and personal funding might be wanted to help such cross-disciplinary work. Organizations equivalent to Headwaters Economics, a non-profit analysis physique based mostly in Bozeman, Montana, that focuses on neighborhood improvement and land administration, are expert at coordinating such initiatives. Collaborations could possibly be motivated by cross-disciplinary periods on wildfires on the annual conferences of organizations such because the American Geophysical Union and the Affiliation of Environmental and Useful resource Economists.
Quantitative fashions are additionally wanted to evaluate the possible outcomes of intervention methods equivalent to laws or incentives associated to constructing supplies, landscaping or insurance coverage. Options have to be devised collectively by all events — throughout academia, business, nationwide and non-profit companions and specialists on the bottom.
Multiteam analysis platforms have to be constructed to discover wildfires. This may be accomplished by initiatives such because the Gordon and Betty Moore Basis’s Wildfire Resilience Initiative, a multidecade funding of greater than US$100 million to align science, expertise and coverage, with the objective of guiding western North America to an period by which society can stay sustainably with hearth.
Scientists should step as much as assist to construct a fire-resilient future, past documenting occasions and assessing dangers. Particular person disasters appeal to consideration, and rightly so, however the focus must be on the best way to coexist with hearth — not merely how greatest to battle it.







