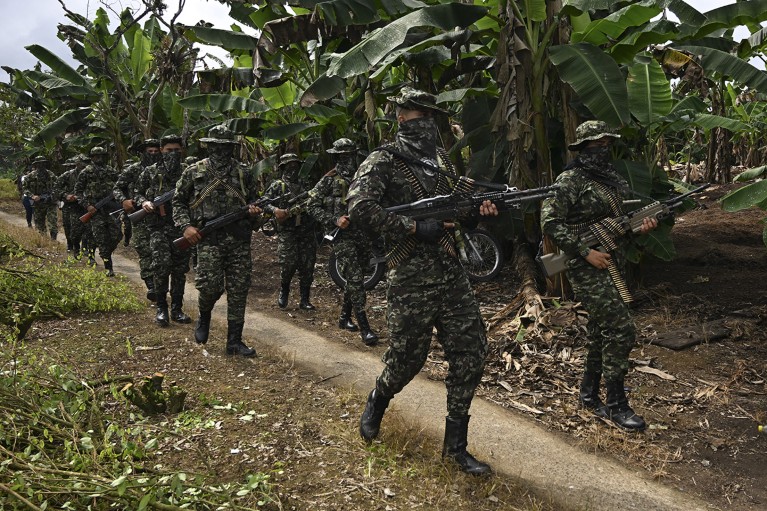

Guerrillas from the FARC motion have been concerned in a long-running battle in Colombia, which is among the world’s most biodiverse nations.Credit score: Joaquin Sarmiento/AFP by way of Getty
Since Russia’s invasion in 2022, 3 million hectares of Ukraine’s protected areas have been affected by navy actions1. For instance, our impartial evaluation of satellite tv for pc imagery reveals that within the Sviati Hory (Holy Mountains) Nationwide Nature Park within the east of the nation, 16% of forested areas have been bodily broken by fires, shelling and the actions of navy automobiles (see ‘Assessing impacts in battle zones’). Protected areas have misplaced their employees and gear, and properties have been broken or destroyed.
Right now, extra armed conflicts are below means than at any level for the reason that Second World Battle. Conservationists and others are more and more investigating the impacts on biodiversity2–4, but governments and conservation organizations have been reluctant to explicitly tackle the problem in conservation coverage. In 2022, when almost 200 nations agreed in Montreal, Canada, on the International Biodiversity Framework — a set of targets supposed to stop catastrophic lack of the world’s biodiversity — armed battle was left unmentioned.
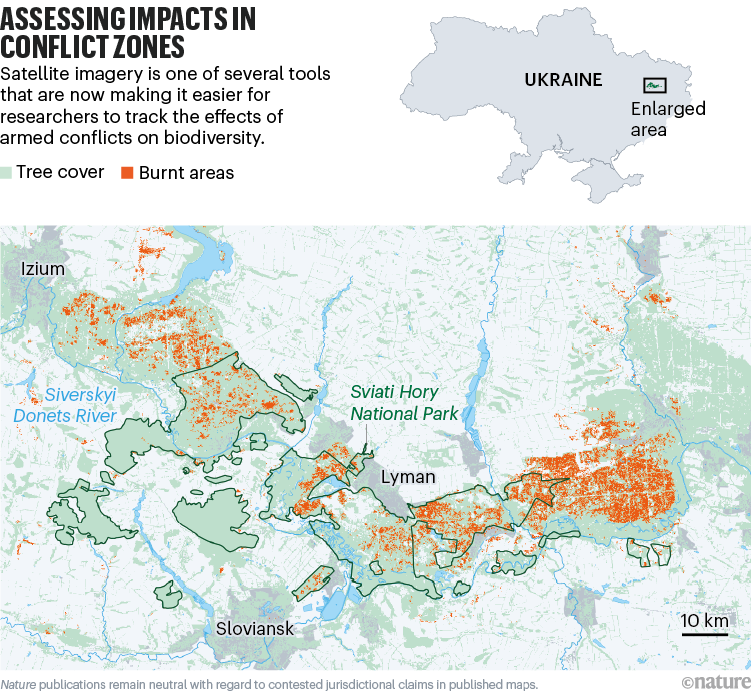
Sources: Land cowl: ESA/OpenStreetMap; Nationwide park boundaries: Emerald Community; Burnt areas: Evaluation by D. Weir et al.
This month, ministers of the setting, conservationists, Indigenous peoples and others are gathering in Cali, Colombia, to assist to translate the biodiversity framework into motion on the sixteenth assembly of the Convention of the Events to the Conference on Organic Range (COP16). Colombia is among the world’s most biodiverse nations. Since 2016, it has additionally been dealing with challenges in implementing a peace settlement signed after 5 a long time of battle, a lot of which was between its authorities and the guerrilla motion FARC.
Linking to the experiences of the Colombian folks, COP16 organizers have specified that the assembly ought to be “a COP of the folks”, and that it ought to prioritize “Paz con La Naturaleza” or peace with nature. In doing this, they’re encouraging attendees to give attention to how the exploitation of pure assets, and the battle that this brings, can hurt biodiversity, in addition to on how interventions to guard biodiversity would possibly assist to foster peace (see go.nature.com/3y95zgv).
We urge world leaders and conservation, humanitarian and different organizations to observe Colombia’s lead and provides better precedence to the influence of armed battle on biodiversity — and to conservation’s function in selling peacebuilding — in analysis and coverage agendas.
What’s identified
Analysis on the consequences of armed conflicts on ecosystems has been restricted for apparent causes. However over the previous decade, using satellite tv for pc imagery, the monitoring of social media and different open-source intelligence, and the growing involvement of native communities in analysis have allowed investigators to enhance monitoring of the influence of armed conflicts in settings which might be troublesome or harmful to work in.
Between 1950 and 2000, greater than 80% of armed conflicts befell in 34 acknowledged biodiversity hotspots5. In line with knowledge printed in July, 39 nations — together with many which might be wealthy in biodiversity, akin to Colombia, Myanmar, Brazil and Cameroon — are at present experiencing sustained or escalating ranges of battle (see ‘Far-reaching results’ and go.nature.com/3btgzrn).
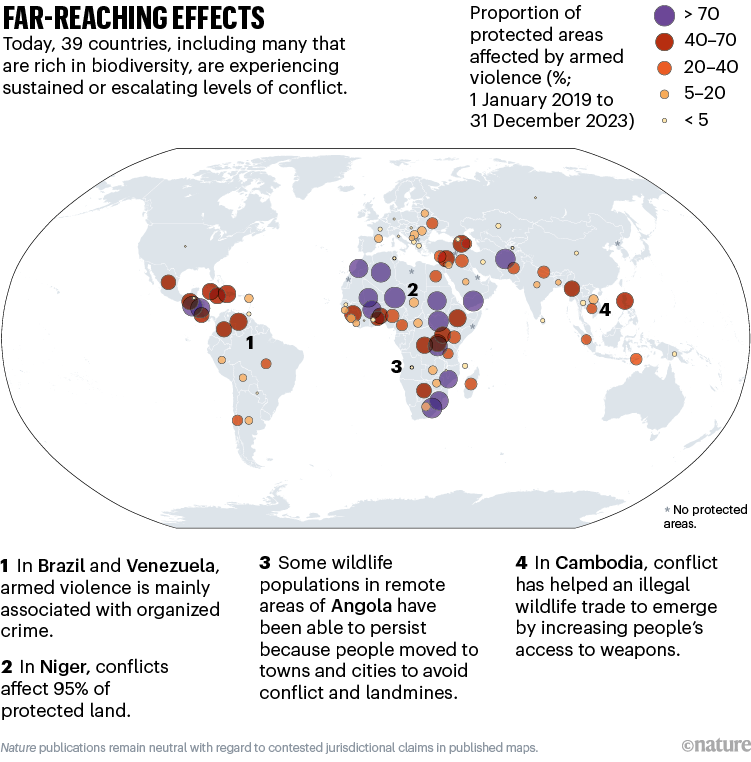
Supply: ACLED Battle Index 2024
The impacts go far past the direct results of warfare. Entry to small arms and lightweight weapons, akin to pistols, rifles and lightweight machine weapons, makes it simpler for folks to kill animals for bushmeat or commerce. Certainly, will increase within the possession of small arms following battle have been implicated within the decline, and in some instances the extinction, of huge mammals throughout the Sahara–Sahel area of Africa6. Battle may even deliver long-term adjustments within the threats to wildlife. In Cambodia, for instance, elevated entry to weapons by means of battle was one issue that allowed an unlawful wildlife commerce to emerge, one which continues to produce worldwide markets with (amongst different gadgets) the physique components of Sunda pangolins (Manis javanica; usually referred to as scaly anteaters) and gaur (Bos gaurus, a wild cattle species) for conventional medication, meat and handicrafts7.
A number of research have proven that unlawful looking and logging usually speed up throughout and after battle — both as a result of governance and establishments are weakened, or as a result of conventional administration methods disappear when persons are displaced8. Likewise, conflicts can enhance folks’s dependencies on wooden for gas and thereby drive overharvesting9.
No foundation for declare that 80% of biodiversity is present in Indigenous territories
The consequences of armed battle on biodiversity will be extraordinarily various, relying on the context. In Angola, nearly three a long time of battle starting within the mid-Seventies displaced thousands and thousands of individuals, which left some areas of the nation comparatively freed from human impacts. Additionally, the widespread use of landmines (that are nonetheless being cleared) prevented folks from returning to massive areas of wilderness. In consequence, sure populations of threatened wildlife species in distant areas of the nation, for instance within the centre and close to the border with Namibia and Zambia, have been in a position to persist10,11.
Conversely, in some areas nearer to city centres, such because the coastal Quiçama Nationwide Park close to the capital Luanda, widespread looking throughout and after battle has led to declines in lots of mammal species12 and possibly to the native disappearance of some species, together with the widespread eland (Tragelaphus oryx) and roan antelope (Hippotragus equinus). And for the reason that battle ceased, massive mammal populations throughout Angola’s wilderness and guarded areas have declined owing to a breakdown in legislation enforcement and governance — disruption that started with the battle however that persists to this present day.
Alongside research of the consequences of battle on biodiversity, there was a rising curiosity in using ‘nature-based options’ to help folks’s well-being and livelihoods throughout and after battle — and to assist keep away from future battle. As a part of the Kibira Peace Forest challenge, which was established in Burundi in 2021, for instance, a coalition of regional and worldwide organizations and donors engaged the federal government, non-public sector and local people — notably ladies — within the stewardship of biodiversity. An evaluation of the challenge means that it strengthened social cohesion and improved folks’s livelihoods, which in flip decreased ranges of battle and deforestation (see go.nature.com/47xztpy).
Placing battle on the desk
Promising as these efforts are, way more analysis is required — for instance, to probe the interactions between biodiversity loss, armed battle and local weather change. There are additionally questions on whether or not Indigenous or community-led administration of pure assets is extra resilient than, say, authorities administration within the face of conflicts. A 2023 research confirmed that on the earth’s biodiversity hotspots, ecosystems on Indigenous peoples’ lands are much less degraded than are these on non-Indigenous lands, though armed battle is extra prone to happen within the former13.
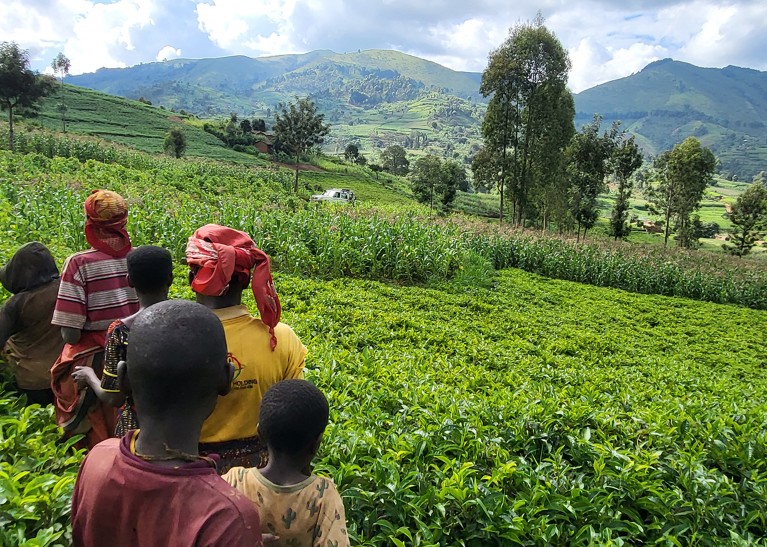

The Kibira Peace Forest challenge in Burundi, funded by the United Nations Nature Facility, engaged native folks in biodiversity stewardship.Credit score: UN Capital Growth Fund
Extra instantly, adjustments to a number of the devices that can be used to implement the International Biodiversity Framework might assist nations to mitigate the impacts of battle on biodiversity, construct biodiversity governance and assist to revive biodiversity following battle.
The Conference on Organic Range is the worldwide treaty that governs the conservation of biodiversity, its sustainable use and the sharing of advantages from using genetic assets. Since getting into into pressure in 1993, it has been ratified by 196 events. However it’s silent on the problem of battle. Additionally, neither the conference’s earlier Strategic Plan for Biodiversity and its accompanying Aichi targets, nor its present International Biodiversity Framework — which lays out 23 actions or targets wanted to guard and restore biodiversity between now and 2030 — tackle the connection between biodiversity and armed battle.
Ditching ‘Anthropocene’: why ecologists say the time period nonetheless issues
In our view, nations ought to be urged to include language that explicitly considers the wants and challenges arising within the face of armed battle — and through peacebuilding — of their Nationwide Biodiversity Technique and Motion Plans (NBSAPs). These lay out the actions that nations will take to deal with threats to biodiversity, and so assist to attain the ambitions of the International Biodiversity Framework. For instance, nations might set out how restoration of biodiversity can be used to construct and maintain peace. International locations might additionally embody plans to watch the influence of armed battle on biodiversity of their NBSAPs. Information on conflicts are already obtainable ought to governments wish to use them, such because the ACLED Battle Index, which is derived from knowledge on incidents of political violence worldwide.
There may be little urge for food for including additional indicators to the official record of greater than 100 that can be used to watch progress in direction of the International Biodiversity Framework’s targets. But the event and future inclusion of indicators that assist governments, scientists and policymakers to measure and perceive the influence of armed conflicts on the setting and biodiversity over time, and therefore their results on nations’ skills to ship on their commitments, might deliver super worth.
Crucially, extra technical and monetary help should be directed in direction of nations affected by battle. That is particularly vital through the early years of restoration following battle, when persevering with insecurity and weak environmental governance can exacerbate deforestation and different threats to biodiversity. The Conference on Organic Range and different worldwide conservation agreements, such because the Ramsar Conference on Wetlands, symbolize automobiles for collating experience, focusing folks’s consideration and mobilizing funding and technical help. These ought to be harnessed particularly for this objective.
Donors usually view conservation tasks in battle areas as too dangerous or too liable to failure. This may imply that group tasks, native non-governmental organizations and front-line employees, akin to rangers, go unsupported. So long as these concerned be certain that they’ve an in-depth understanding of the native context, and prioritize the native possession of tasks and useful resource administration, a shift in mindset would allow the expansion of sustainable, impactful conservation tasks to mitigate the consequences of battle on biodiversity, and to assist to foster peace.
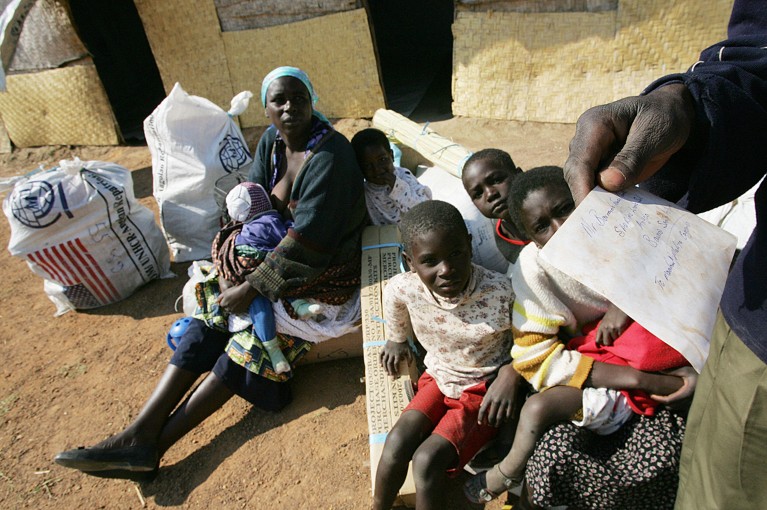

Refugees from Angola who fled the nation throughout its 27-year civil struggle have been in a position to return after a peace accord was signed in 2002.Credit score: Alexander Joe/AFP by way of Getty
Influential organizations are starting to make headway on this entrance. In 2020, the International Setting Facility, one of many largest worldwide donors supporting biodiversity tasks, reviewed its portfolio of tasks in ‘fragile states’ (nations with weak governance, persistent humanitarian crises, persistent social tensions and so forth) and in nations coping with ongoing battle. It recognized that ‘conflict-sensitive’ approaches may also help to enhance the outcomes of conservation tasks, and has since been working to replace its practices accordingly14. Elsewhere, partnerships between conservation and peacebuilding organizations, akin to between Conservation Worldwide in Arlington, Virginia, and the PeaceNexus Basis close to Geneva, Switzerland, are starting to offer insights that could possibly be utilized extra broadly to tasks in difficult settings15.
In the end, a lot better consciousness is required of the impacts of battle on biodiversity. Incorporating the problem into the implementation of the International Biodiversity Framework could be an efficient method to obtain this, notably as a result of battle reduces the capability of nations to collect and collate knowledge on biodiversity. Elevated consciousness might additionally create alternatives for different organizations to interact, from United Nations peacekeepers to humanitarian organizations. For example, organizations that clear landmines, akin to Norwegian Folks’s Assist in Oslo, are already more and more analyzing how you can mitigate the influence of their actions on delicate habitats.
Following Colombia’s lead
There may be now consensus amongst scientists and most governments that wholesome ecosystems are essential for safeguarding human rights, livelihoods and well-being. Though there’ll at all times be limits to the diploma of environmental safety that may be achieved in struggle zones, there are enormous alternatives to cut back environmental hurt stemming from battle, to make sure that biodiversity safety in post-conflict restoration efforts turns into mainstream, and to make sure that the setting is built-in into peacebuilding processes.
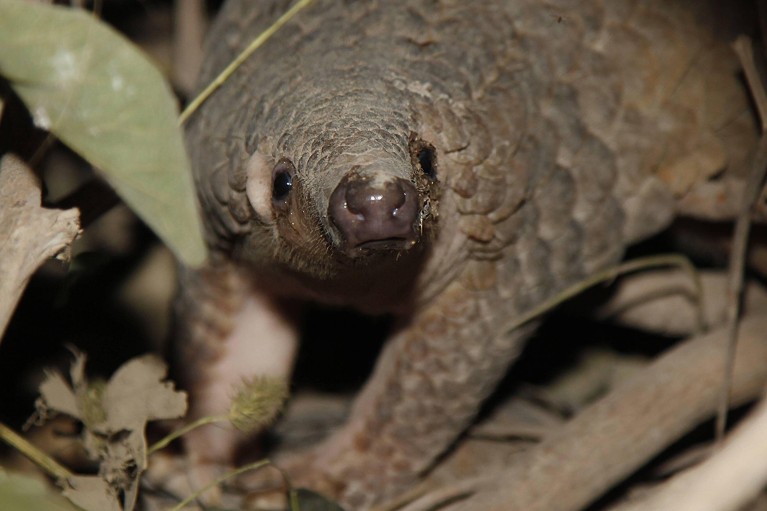

An unlawful wildlife commerce in Cambodia — pushed partly by elevated entry to weapons by means of battle — provides worldwide markets with the physique components of Sunda pangolins (Manis javanica).Credit score: Imago/Alamy
A number of elements have inspired Colombia’s COP16 organizers to push the problem on the upcoming assembly. Colombia has endured one of many longest armed conflicts in Latin America, which has been fuelled largely by illicit economies underpinned by pure assets, akin to gold and timber, in flip severely harming biodiversity. Even right this moment, ecosystems and native communities, together with Indigenous peoples, Afro-Colombians and campesinos (small farmers), are trapped within the center. And though deforestation within the nation was decreased by 36% in 2023 due to collaborative work between communities, civil society and the federal government to guard forests from exploitation, escalating threats to leaders of social and environmental actions might drive charges up once more. Within the first 9 months of 2024 alone, 117 such leaders have been murdered in Colombia.
The hyperlinks between Colombian biodiversity and battle are so robust that the setting is included within the nation’s Particular Jurisdiction for Peace (Jurisdicción Especial para la Paz; JEP). The JEP is a transitional-justice mechanism that was launched in 2017 as a part of the peace settlement between FARC guerrillas and the federal government. In 2019, the federal government declared that the setting had been a “silent sufferer of the battle” and that it might examine reparation mechanisms for the injury prompted.
In opposition to a backdrop of such experiences — which aren’t distinctive to Colombia — the nation’s two-year presidency of the Conference on Organic Range provides an unprecedented alternative to ultimately deliver consideration to the interactions between biodiversity, battle and peace.




