Nobody seen when an previous pipe began spewing methane into the sky within the British countryside. The leak, close to a railway line and landfill web site in Cheltenham, UK, launched greater than 200 kilograms of methane an hour, but the invisible fuel went undetected. That was till Emily Dowd, a local weather scientist on the College of Leeds, UK, noticed the leak in March 2023 whereas trying by means of observations from a passing satellite tv for pc. “It was utterly by likelihood,” she says.
Nature Highlight: Area analysis
Dowd had been monitoring the landfill web site utilizing knowledge from a methane-detecting satellite tv for pc 500 kilometres above Earth, constructed by GHGSat, primarily based in Montreal, Canada. Over the subsequent 11 weeks, she labored with different scientists to establish the precise location of the leak and alert the utility firm accountable. “We noticed it till it was fastened in June,” she says. Between the time the leak was found and when it was fastened, Dowd says, the vitality within the methane launched was equal to the electrical energy utilized by 7,500 houses over one 12 months.
Methane is chargeable for round 26% of the post-industrial rise in world temperature. Carbon dioxide accounts for an extra 70%, and the remaining is attributable to different greenhouse gases, together with nitrous oxide. However methane’s quick lifespan of a few decade within the ambiance, paired with its substantial warming impact, makes it a extra quick goal in tackling local weather change. “If we cut back our emissions of methane, it buys us time while we cut back our CO2 emissions,” says Dowd.
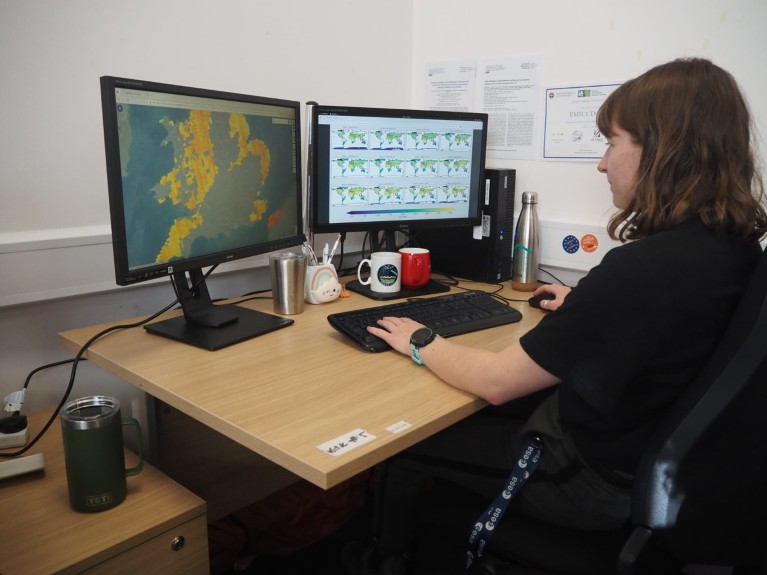

Local weather scientist Emily Dowd analyses knowledge from the TROPOMI instrument on the sentinel-5P satellite tv for pc.Credit score: Benjamin Wallis
The Cheltenham incident highlights the rising energy of satellites to pinpoint the sources of emissions from area. Though satellites have monitored Earth’s local weather for many years, there’s an growing demand to localize these observations and establish unintended leaks, or nefarious releases, from particular person websites and services. “We need to make these emissions seen so ignorance can now not be used as an excuse for inaction,” says Riley Duren, chief govt of Carbon Mapper, a non-profit group primarily based in Pasadena, California.
Methane metrics
A lot of the present give attention to methane was pushed by COP26, the 2021 United Nations Local weather Change Convention in Glasgow, UK, at which international locations signed a pledge to scale back methane emissions by no less than 30%, relative to 2020 ranges, by 2030. “Issues have developed significantly post-COP26,” says Jean-Francois Gauthier, GHGSat’s senior vice-president of technique. “Many have referred to COP26 because the ‘methane second’.” There at the moment are 155 international locations signed as much as the pledge, representing half of all world methane emissions.
Between 8% and 12% of methane emissions within the oil and fuel business come from ‘tremendous emitters’, plumes of methane that may be launched at charges exceeding 100 kilograms an hour, much like the leak that Dowd recognized in Cheltenham. Tremendous emitters have quite a lot of sources, together with extinguished natural-gas flares that proceed to launch fuel, in addition to landfill and livestock. Figuring out and halting these plumes is one method to have a rapid-fire affect on methane emissions.
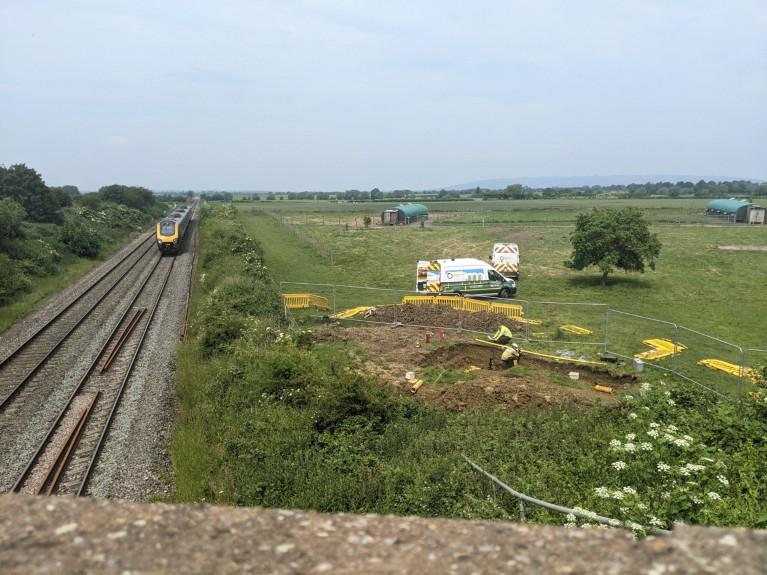

Work is performed on the web site of the Cheltenham fuel leak in 2023.Credit score: Emily Dowd
Efforts to take action are beneath manner utilizing quite a few satellites. GHGSat operates a constellation of 11 satellites to watch methane plumes, and that quantity is about to rise to round 40 by 2027, says Gauthier. NASA’s Earth Floor Mineral Mud Supply Investigation instrument (EMIT), on board the Worldwide Area Station, can observe methane plumes, as can the European Area Company’s TROPOMI instrument on its Sentinel-5P satellite tv for pc.
Every of those services screens methane plumes in several methods. Some are high-resolution and may goal particular person services; the GHGSat constellation, for instance, can monitor emissions as small as 100 kilograms per hour at a decision of 25 metres. Others, comparable to TROPOMI, see a a lot wider subject of view.
In 2021, researchers used knowledge from TROPOMI to detect 2,974 plumes of methane being emitted at charges in extra of 8 tonnes per hour across the globe1. Of the international locations noticed, Turkmenistan had the very best variety of detectable plumes, with 457 (see ‘Plume for thought’).
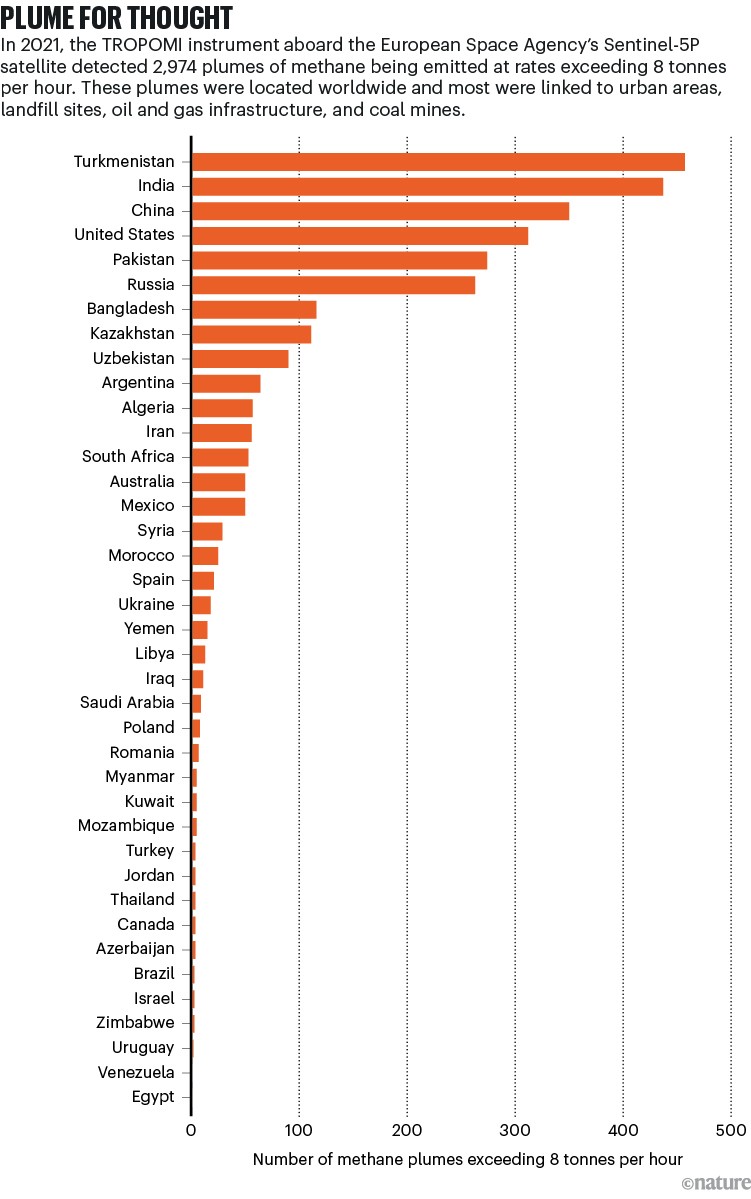
Supply: Ref. 1
This heightened scrutiny might need influenced Turkmenistan’s shock announcement on the 2023 COP28 local weather talks in Dubai, United Arab Emirates, that it could be a part of the pledge to sort out methane emissions. “That’s one thing that was unthinkable years in the past,” says Gauthier, noting that international locations in Central Asia had beforehand been “fairly reluctant to debate this” for worry of being “named and shamed for his or her giant emissions”.
GHGSat positioned greater than 15,800 plumes throughout 85 international locations in 2023, 33% of which originated in Central Asia. Though no satellite tv for pc has mapped all the methane plumes to particular person level sources, knowledge from the persevering with launches of methane-hunting satellites might carry scientists nearer to this objective.
Measured options
The inflow of methane-hunting satellites is equipping regulators with the instruments for motion.
The US Environmental Safety Company (EPA) has finalized its Tremendous Emitter Program, which is able to enable it to make use of knowledge from corporations comparable to GHGSat to watch oil and fuel services for super-emitter occasions — methane releases of 100 kg hr−1 or extra. Operators of these services will likely be given a short while window to conduct their very own investigation into the leak and take corrective motion, or threat fines primarily based on the quantity of methane launched. The programme is anticipated to be up and operating by 2025, when fines will likely be levied at US$1,200 per 1,000 kg of methane emitted
Ethan Shenkman, an environmental lawyer at Arnold and Porter in Washington DC, says that having high-quality knowledge from satellites will likely be essential on this course of. “This programme goes to be one of many key mechanisms for bringing satellite tv for pc knowledge to [focus] on explicit services,” says Shenkman.

GHGSat senior vice-president Jean-Francois Gauthier says that methane-emissions monitoring is a fast-evolving subject.Credit score: GHGSat, Inc.
How satellite tv for pc knowledge are used to crack down on methane emissions will in all probability differ in every area. “The authorized state of affairs in each nation is completely different, so how they are going to implement it will likely be completely different,” says Beth Greenaway, head of Earth commentary and local weather on the UK Area Company, noting that the USA “is a really, very large driver”.
Some satellite tv for pc operators are utilizing this elevated give attention to methane as a enterprise alternative, alongside preventing local weather change. GHGSat sells its knowledge to corporations in order that they will establish leaks or faults of their services and deal with them with none involvement from regulators. “Clients pay us as a monitoring service, and we offer them with common alerts and stories,” says Gauthier. The corporate’s final objective is to “control each industrial emitter every day”, which GHGSat hopes to realize with its deliberate constellation of 40 satellites.
Even with out efforts such because the EPA’s Tremendous Emitter Program, Eric Kort, a local weather scientist on the College of Michigan in Ann Arbor, says that the proliferation of satellites to watch plumes might function a deterrent for dangerous actors earlier than any regulatory motion is required, each in the USA and throughout the globe. “If somebody’s going to cross overhead, you may pay slightly bit extra consideration to creating certain your flare stays lit, or your valve hatch in your tank stays closed,” he says. “Shining the sunshine is a robust instrument.”



