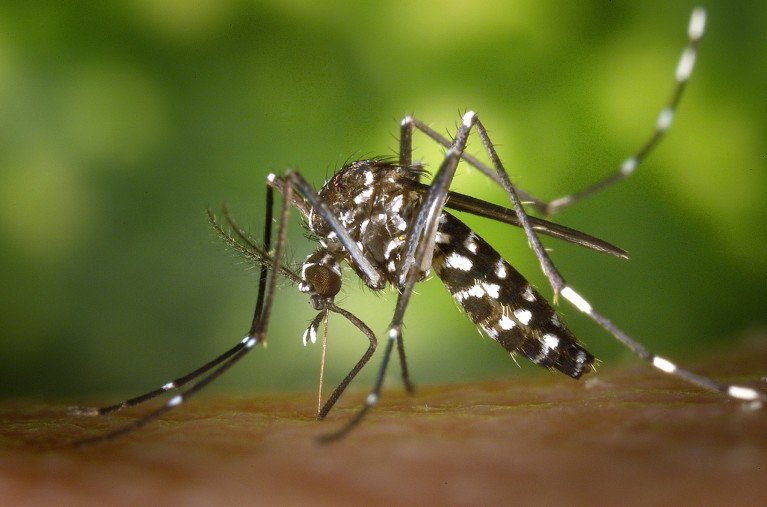
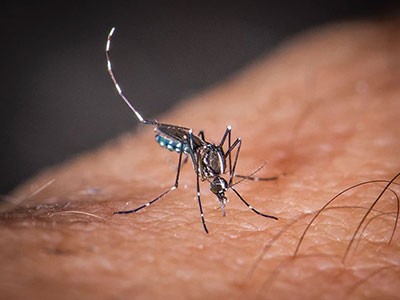
The Asian tiger mosquito (Aedes albopictus) is well recognized by its black-and-white-striped legs.Credit score: James Gathany/CDC by way of Smith Assortment/Gado/Getty
Local weather change is popping Europe right into a breeding floor for mosquito-borne illnesses, researchers warn. Longer summers, hotter temperatures and heavy rainfall are creating beneficial situations for mosquitos in locations the place they couldn’t beforehand thrive.
Figures printed final week by the European Centre for Illness Prevention and Management (ECDC) present that there have been 715 domestically acquired instances of West Nile virus (WNV) throughout 15 nations in Europe to date this yr, surpassing the quantity reported in the identical interval final yr and Europe’s 10-year common. As of 4 September, 51 individuals had died on account of the an infection.
Tropical illnesses transfer north
“This has develop into the brand new regular,” says Céline Gossner, a specialist in rising and vector-borne illnesses on the ECDC in Stockholm, Sweden. The variety of instances of WNV is prone to rise all through September and October, she provides.
Researchers say individuals who reside in areas the place outbreaks have been reported ought to take precautions to keep away from mosquito bites.
“We’re confronted with an issue the place new locations may develop into hotspots of transmission that weren’t ready for this earlier than,” says Houriiyah Tegally, a genomic epidemiologist at Stellenbosch College in South Africa.
Lethal fever
About 20% of WNV infections end in West Nile fever, which causes fever, complications, vomiting and fatigue. In lower than 1% of instances, the illness causes neurological issues, which might embrace a life-threatening swelling of the mind.
“Usually, most of us have an immune system that simply knocks it out,” says Stephen Wealthy, a medical zoologist on the College of Massachusetts Amherst. However older individuals and people with compromised immune techniques are susceptible to more-severe issues, he provides. In Europe, a lot of the reported instances are in individuals aged over 65 years.
The Culex pipiens mosquito, which transmits WNV from contaminated birds to people and different animals — notably horses — is native to Europe, and the virus has been current on the continent because the Nineteen Fifties. However local weather change has led to prolonged transmission intervals and has meant that extra areas are going through outbreaks, together with areas that haven’t reported WNV infections earlier than. “When these viruses unfold in communities that don’t have any earlier immunity, then you’ll be able to see giant outbreaks,” says Rachel Lowe, a local weather and well being scientist on the Barcelona Supercomputing Heart in Spain. A research printed earlier this yr concludes that local weather change facilitated the spatial unfold of WNV in Europe1.
How local weather change is hitting Europe: three graphics reveal well being impacts
Hotter situations have additionally allowed the Asian tiger mosquito Aedes albopictus, which transmits the ‘tropical’ illnesses dengue and chikungunya, to develop its vary. The species has now develop into established in 13 European nations and has been launched to 7 others. Each illnesses are spreading in consequence: this summer season, Italy and France reported 22 domestically transmitted instances of dengue, and a chikungunya case has been detected in France.
Because the variety of heat and moist days will increase, mosquitoes — which flourish in these situations — are “spreading to greater latitudes and in addition greater altitudes”, says Lowe.
Though local weather change is a vital driver of the illness outbreaks, it’s not the only real perpetrator. Elevated journey, particularly after the COVID-19 pandemic, is aiding the dtransmission of viruses throughout borders. The rise in dengue instances in Europe is partly a aspect impact of file outbreaks in different elements of the world: South and Central America are at present battling their worst-ever dengue season, with instances in 2024 already round 230% greater than they had been on the identical time final yr.
A July preprint, on which Tegally is a co-author, discovered that dengue virus strains in Ethiopia intently resemble these in Italy’s 2023 outbreak2. “It’s unattainable to show the directionality of this motion,” says Tegally. However this “tells us that the world could be very linked, and Europe may at one level, if not already, act as a supply of those arboviruses as nicely, as a result of there’s native transmission”.
Don’t get bitten
With mosquito-borne illnesses on the rise in areas the place they’ve beforehand been unusual, researchers say individuals ought to take care to keep away from being bitten, through the use of repellent, sporting long-sleeved, light-coloured clothes and holding home windows lined with mosquito screens.
Making certain there is no such thing as a stagnant water in city gardens, plant pots or flower vases additionally helps by lowering the variety of potential breeding websites, says Lowe. The Asian tiger mosquito is well recognized by its black-and-white-striped legs, she provides.
Dengue is spreading in Europe: how fearful ought to we be?
Scientists additionally warn in regards to the danger of asymptomatic carriers unknowingly contaminating blood banks with illnesses akin to WNV after they donate blood. “Whereas the chance is nicely contained in a roundabout way, as a result of now we have numerous checks and procedures, it’d have an effect on the provision of blood provides and organ provides”, says Celine. The US Facilities for Illness Management and Prevention discovered that 190 blood donors examined constructive for WNV in the US this yr.
Rising dangers like this spotlight the necessity for cautious surveillance of mosquito-borne illnesses, even in areas the place they don’t seem to be endemic.
“There may be at all times the chance of the emergence of a brand new vector-borne illness,” says Gossner. “We have to be ready.”