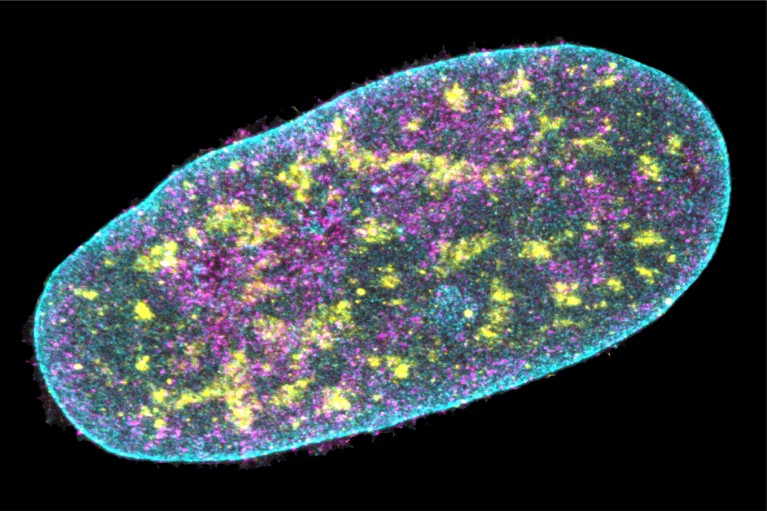
An imaging methodology reveals numerous proteins (blue, yellow and magenta) contained in the nucleus of a human connective-tissue cell.Credit score: Ajay Labade, Zachary Chiang, Caroline Comenho and Jason Buenrostro
Researchers are queuing as much as attempt a strong microscopy approach that may concurrently sequence a person cell’s DNA and pinpoint the situation of its proteins with excessive decision — all with out having to crack the cell open and extract its contents. Imaging DNA and proteins inside intact cells offers essential details about how these molecules work collectively.
The tactic’s builders have already used it to review how ageing may alter the way in which that proteins within the nucleus work together with chromosomes. Because the physique ages, they discovered, adjustments in these nuclear proteins may suppress gene exercise.
“This paper is basically extraordinary,” says Ankur Sharma, a most cancers biologist on the Garvan Institute of Medical Analysis in Sydney, Australia, who was not concerned within the research however is eager to make use of the method to review most cancers cells and described it as “phenomenal” on the social media platform, X.
The tactic, known as growth in situ genome sequencing, was described in a preprint1 posted on bioRxiv on 26 September. It has not but been peer reviewed.
DNA packaging
The method may very well be significantly helpful to researchers who’re finding out how DNA is wound round proteins and stuffed into the nuclei of cells — and the way the situation of genes inside that morass can have an effect on their exercise. We are able to consider DNA as “a linear string of knowledge that must be squished and arranged inside a 5-micron-sized cell nucleus”, says Jason Buenrostro, a geneticist at Harvard College in Cambridge, Massachusetts, and an creator on the preprint. “There’s numerous data in how that folding occurs.”
To extract that data, Buenrostro and his colleagues blended two beforehand reported strategies. One feeds the cell a particular enzyme for copying DNA, along with a collection of fluorescently tagged DNA parts to be included, one after the other, into the rising DNA strands. By studying the sequence wherein the fluorescent tags are added, researchers can decide the sequence of fragments of the genome2.
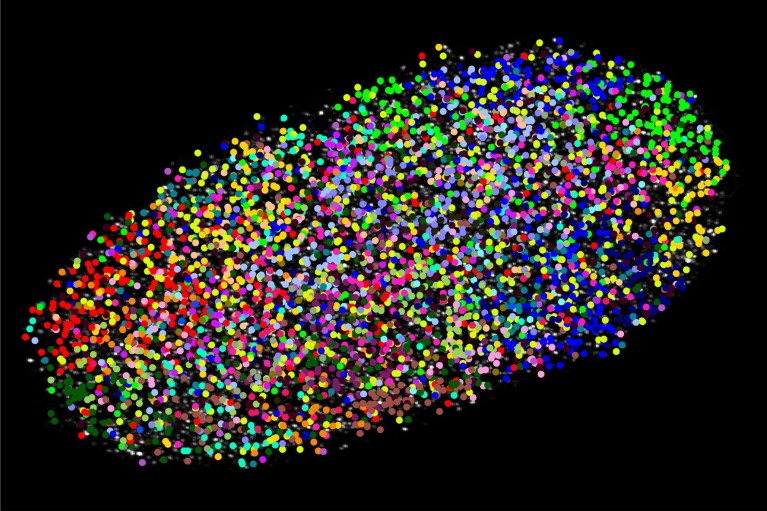
The brand new imaging approach may also be used to show genomic data. Every color represents a special chromosome within the nucleus of the identical connective-tissue cell proven above.Credit score: Ajay Labade, Zachary Chiang, Caroline Comenho and Jason Buenrostro
Researchers have lengthy recognized find out how to label proteins with tags to trace their places. However the decision of gentle microscopy is restricted by the wavelength of sunshine, which makes it tough to differentiate fluorescently tagged strands of DNA or proteins which are very shut collectively. This poses a specific downside within the slim confines of the nucleus.
So the crew added one other methodology known as growth microscopy3. This system depends on a gel that permeates cells after which swells when it absorbs water — very similar to the filling in disposable diapers. Because the gel expands, it pushes molecules additional aside, making it simpler to differentiate one protein molecule from each other.
The wedding of the 2 strategies allowed Buenrostro’s crew to review interactions between proteins and genes within the cells of individuals with Hutchinson–Gilford progeria syndrome, a genetic situation that leads to untimely ageing. This situation is attributable to mutations in proteins known as lamins, that are normally discovered on the periphery of cell nuclei. The researchers confirmed earlier outcomes suggesting that in people with progeria, these irregular lamins intrude into the inside of the nucleus, the place they appear to change the standard association of chromosomes and suppress gene exercise. Related abnormalities have been current in pores and skin cells from a 92-year-old donor who didn’t have progeria.
Data goldmine
Growth in situ genome sequencing is the most recent in a sequence of strategies which are permitting researchers to gather an rising quantity of information from particular person cells. The last word purpose is to develop an method to detect practically any protein or metabolite within the cell, says Thierry Voet, a geneticist at KU Leuven in Belgium.
How one can make spatial maps of gene exercise — all the way down to the mobile stage
For now, Voet and his crew are contemplating whether or not the strategy may very well be used of their research of how cells in a growing embryo can address having completely different numbers of chromosomes from each other.
The approach requires appreciable experience, and it will restrict the variety of researchers who can instantly take it up, says Kelly Rogers, who research superior microscopy on the Walter and Eliza Corridor Institute of Medical Analysis in Melbourne, Australia. “It undoubtedly seems to be difficult.”
Even so, Rogers can checklist loads of colleagues who may wish to harness the method. With time, she says, the protocols may very well be streamlined and even commercialized.
“One factor that’s for positive is that it will turn into extra accessible by a broader vary of scientists,” says Rogers. “There don’t appear to be many limits now to what we will obtain.”