This month, world leaders are gathering on the 79th session of the United Nations Basic Meeting in New York to debate the issue of micro organism, fungi and protozoans more and more evolving resistance to antimicrobial medicine. Traditionally, options have centered on high-income international locations, though 4.3 million of the estimated 5 million deaths related to infections of drug-resistant micro organism happen in low- and middle-income international locations. Forward of the UN assembly, 4 specialists — from Bangladesh, Brazil, Nigeria and the Center East — instructed Nature which modifications might be most important the place they dwell.
SENJUTI Saha: Bangladesh

Senjuti Saha sees the necessity for a worldwide dedication to help knowledge assortment on resistance.Credit score: Vivan Mehra
For greater than a decade, I’ve seen the affect of antimicrobial resistance (AMR) on folks, significantly newborns, at first hand. Bangladesh Shishu Hospital and Institute in Dhaka — one of many collaborating organizations of the Little one Well being Analysis Basis, the place I work — is the nation’s largest kids’s hospital. Right here, six out of each ten infants with infections attributable to multidrug-resistant Klebsiella pneumoniae micro organism die, typically just some days after being contaminated.
In Bangladesh, a serious problem within the struggle towards AMR is the shortage of information on which micro organism are infecting whom, on how the varied strains reply (or not) to which antibiotics and on how selections are made about which medicine to make use of.
Cease delaying motion on antimicrobial resistance — it’s achievable and reasonably priced
Bangladesh’s health-care system is uncommon in that most individuals obtain remedy in group clinics, diagnostic centres and pharmacies somewhat than in hospitals. Folks are inclined to go to hospitals solely when remedy obtained from these different locations fails. However as a result of a lot of the nation’s AMR knowledge come from hospitals, authorities officers, clinicians and microbiologists have a skewed understanding of the issue.
Because of biases within the out there knowledge, many individuals assume, as an example, that resistance is ubiquitous. Physicians typically give sufferers late-generation or last-resort antibiotics though early-generation medicine may nonetheless work. This in itself could be worsening resistance.
One other situation that impacts Bangladesh particularly is the shortage of protocols and fundamental interventions in and round well being care that, if applied, would drastically enhance the scenario.
For the infants at Shishu hospital, the best method to saving lives is stopping infections from taking maintain within the first place. Methods that might considerably cut back AMR embody investing in parental vitamin throughout gestation (which, in flip, would enhance infants’ delivery weights and cut back their susceptibility to an infection), making certain that pregnant folks obtain antenatal and perinatal care and selling supply practices that reduce the chance of infants (and birthing mother and father) getting infections.
What’s wanted in Bangladesh — and in low- and middle-income international locations extra broadly — is a worldwide dedication to help analysis and knowledge assortment on AMR, and funding within the fundamental interventions that can cut back it.
ANA CRISTINA GALES: Brazil

Ana Cristina Gales thinks that even small modifications will be transformative for Brazil.Picture courtesy of Ana Cristina Gales
5 years in the past, a 15-year-old boy was introduced into the hospital the place I work in São Paulo, Brazil, after growing an an infection. He had lower his ankle whereas retrieving a kite from a stream. The boy developed a extreme, systemic an infection attributable to methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus and died round 5 weeks after being admitted.
That boy caught in my thoughts, as a result of he was across the age of my two daughters on the time. As a advisor in infectious illnesses, I’ve seen too many individuals affected by AMR. Probably the most irritating points is that this devastating downside could possibly be drastically lowered with comparatively easy measures1.
Points that have an effect on hospitals in Brazil — and in lots of different international locations — embody employees members failing to maintain surfaces and their palms clear, and failing to isolate folks contaminated with micro organism which can be immune to antimicrobial medicine. Some folks must spend days ready for beds on stretchers in hospital corridors, making it more durable for health-care employees — who are sometimes overworked — to implement fundamental measures to forestall and management infections. The truth is, over the previous twenty years, investigators have described a number of instances during which equivalent antimicrobial-resistant micro organism (of the identical clone) have been present in distinct hospitals2 — the implication being that resistant micro organism are being transferred between establishments, maybe by the motion of sufferers.
However as illustrated by the case I described, AMR doesn’t happen solely in hospital settings. And in Brazil, one of many largest challenges is folks’s failure to acknowledge AMR as a public-health downside. Most individuals who don’t work in hospitals lack the information wanted to know what AMR is and the way it may have an effect on their well being. The nation is battling endemic illnesses, similar to malaria, leishmaniasis and Chagas illness. And over the previous 10 years, Brazil has skilled quite a few epidemics attributable to mosquito-borne viruses, together with Zika, chikungunya, yellow fever, dengue and, most not too long ago, Oropouche fever. Such illnesses are inclined to obtain extra consideration than does AMR, which is more durable for folks to pin to a selected trigger.
Antibiotic resistance is a rising menace — is local weather change making it worse?
So long as AMR isn’t seen as a major well being menace at a societal stage, it is going to proceed to be neglected by policymakers and politicians. Extra positively, nonetheless, Brazil has huge potential to scale back AMR, as a result of it has a common, decentralized health-care system in place for bringing medical interventions to everybody. It additionally has nationwide programmes that present folks with vaccines and drugs to deal with HIV and hepatitis at no cost. Furthermore, as one of many world’s largest producers of animal protein, Brazil may assist to steer the discount of antimicrobial use in livestock rearing. The truth is, over the previous decade or so, Brazil has already made some key advances on the subject of tackling AMR.
Since a regulation was launched in 2010, folks have been in a position to purchase antibiotics (for human use) solely with a medical prescription. Over the previous few years, the federal government has invested tens of millions of US {dollars} in analysis on AMR — and in surveillance, each in state laboratories and in hospitals. Moreover, Brazil has developed a nationwide plan to scale back the issue utilizing a multisectoral and transdisciplinary ‘One Well being’ method, which is at present below evaluate.
Remodeling this plan right into a profitable programme, just like the nation’s vaccination, HIV and hepatitis schemes, would require extra political buy-in and much more funding in efforts to lift public consciousness. It’s going to additionally require the mixing of priorities throughout human, animal and environmental well being. However clinicians, scientists, authorities officers and others don’t want entry to superior applied sciences and new antimicrobials to make an unlimited distinction. A couple of, comparatively easy modifications could possibly be transformative: extra mother and father and different caregivers vaccinating kids; extra folks avoiding using antimicrobials when they’re pointless, similar to these used to deal with viral respiratory infections; and increasing the nation’s fundamental sanitation programme, so that each Brazilian metropolis treats its sewage earlier than releasing it into the surroundings.
IRUKA N. OKEK: Nigeria

Improved entry to well being care might help to scale back antimicrobial resistance, says Iruka Okeke.Credit score: Science for Africa Basis
Most Nigerian folks have a extreme bacterial an infection or malaria a minimum of annually. In order that they have an actual in addition to a perceived want for antimicrobials. However persons are typically unable to acquire those they want, or they use antimicrobials with out recommendation from health-care suppliers. (In 2019, solely 41% of Nigeria’s inhabitants may entry well being care simply.) Usually, physicians don’t have entry to the diagnostic instruments wanted to tell their selections about what antimicrobials folks ought to take, or people can’t afford these particular medicine. So, though in lots of settings using antimicrobials is extreme or inappropriate, in Nigeria, bettering folks’s entry to well being care and drugs should be a part of any plan to handle AMR.
An article within the Lancet Collection on Antimicrobial Resistance revealed in Could1 proposes that authorities ought to intention to scale back the variety of deaths attributable to AMR by 10% and the inappropriate use of antibiotics in people and different animals by 20% and 30%, respectively, by 2030. I’m satisfied that Nigeria may meet these targets utilizing instruments out there right this moment.
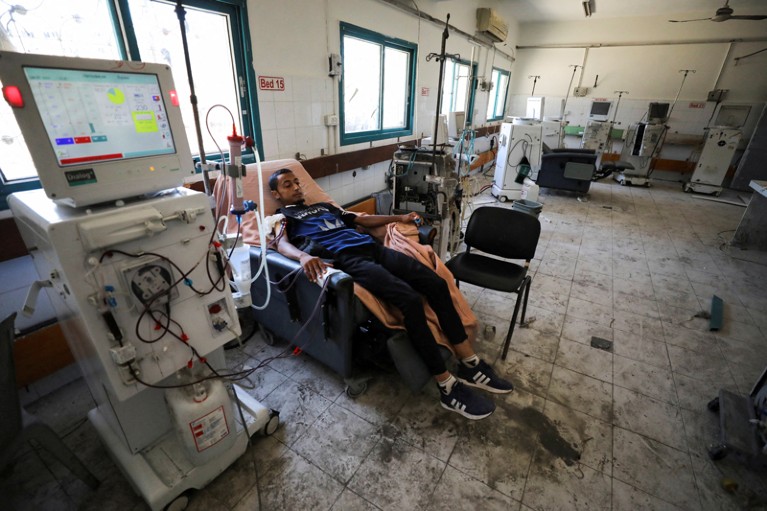
A affected person receives dialysis in June at Al-Shifa hospital in Gaza Metropolis, which was broken through the Israel–Hamas battle.Credit score: Dawoud Abu Alkas/Reuters
One-quarter of Nigeria’s inhabitants defecates outdoors, similar to in fields, gutters and forests, as an alternative of utilizing a rest room, some or the entire time. And knowledge from a 2024 report3 I used to be concerned in present that the majority metropolis residents depend on family water from wells or boreholes that’s contaminated by faeces. That is the case in Ibadan, the place I dwell. Brokers of illness — together with typhoid, diarrhoea and cholera — can unfold simply, as can non-harmful (commensal) organisms harbouring resistance genes that may be transmitted to pathogenic micro organism. One such commensal microorganism is Escherichia coli, which is usually discovered within the gut. Offering folks with protected water and higher sanitation may cut back the affect of each enteric infections (abdomen or intestinal diseases attributable to microbes, similar to viruses, micro organism and parasites) and AMR concurrently, yielding an estimated return of US$5 or extra for each $1 spent4.
Modest funding may additionally enhance an infection prevention and management practices at health-care services — similar to selling handwashing or the isolation of individuals contaminated with antimicrobial-resistant micro organism. In 2020, the Nigeria Centre for Illness Management and Prevention launched up to date tips on an infection management and prevention. A modelling research5, revealed in Could as a part of the Lancet sequence, signifies that by following such tips judiciously, health-care suppliers may forestall antimicrobial-resistant infections in health-care settings, which at present account for about 300,000 deaths worldwide.
The struggle towards antimicrobial resistance
Nigeria has been rolling out pneumococcal vaccines since 2014 and rotavirus vaccines since 2022. However protection, at present at 60% and 49%, respectively (in line with knowledge from the United Nations’ kids’s charity UNICEF), must be prolonged. Malaria and typhoid-conjugate vaccines are but to be deployed. Furthermore, a worldwide scarcity of cholera vaccines has hampered their use in current outbreaks. All of those vaccines may cut back ranges of AMR — by reducing the possibility of problems arising that contain bacterial infections, and of individuals administering antibiotics inappropriately. In keeping with the modelling research within the Lancet sequence, vaccines may forestall round 180,000 deaths related to AMR yearly5.
In 2017, Nigeria launched an AMR surveillance system. As soon as this technique covers a larger geographical space and extra complete knowledge are collected — from folks, animals and the surroundings — investigators will be capable to quantify the impacts of every of those instruments and help the prioritization of interventions for nationwide deployment.
NOUR SHAMAS: Center East

Humanitarian reduction efforts ought to prioritize an infection surveillance, says Nour Shamas.Credit score: Aziz Reguig
I’m always worrying about whether or not my mom, who has a recurrent an infection of the urinary tract (which is immune to most antibiotics), will be capable to hold accessing the health-care companies and antibiotics she wants. She lives in Beirut, Lebanon, and I’m at all times reminding her to maintain her passport and antibiotics at hand in case she has to flee within the face of a army assault.
The impacts of political and financial instability and battle are sometimes neglected when folks think about the elements contributing to AMR. However it’s a lot more durable to implement and preserve the forms of intervention typically really helpful to mitigate resistance, similar to restrictions that restrict over-the-counter meting out of antimicrobials, in Lebanon and different japanese Mediterranean international locations which can be experiencing ongoing battle. The truth is, such an intervention may restrict entry to lifesaving antimicrobials for many who can’t in any other case get hold of them.
The destruction of health-care services, faculties and different infrastructure in addition to folks’s livelihoods, and the displacement of each native folks and refugees, present a perfect surroundings for AMR to extend. In these locations going through battle or receiving refugees, dwelling areas have gotten more and more crowded. Many individuals have misplaced entry to wash water and sanitation, well being care, drugs and vaccinations. Most have misplaced wages and lots of are now not in a position to get hold of ample vitamin, and persons are extra probably to make use of antimicrobials inappropriately — if they’ll pay money for them.
Though funding should be made globally in interventions to mitigate resistance, I urge all funders and assist organizations to issue AMR into humanitarian reduction efforts. Extra analysis should be performed on the affect of AMR on communities dwelling in conflict-affected areas, and on context-specific options. Further assets should be dedicated to bettering provide chains and entry to antimicrobials and diagnostic instruments, and to bettering their use in these areas. And AMR surveillance, an infection management and well being techniques as a complete should be strengthened in conflict-affected areas.





