The irregular tissues vary from black blisters to pink nodules and white-hot cysts. They develop all through the pelvic cavity, latching on to the ovaries and peritoneum or infiltrating the bowel and bladder.
As soon as detected, the painful lesions of endometriosis, an inflammatory situation, will be eliminated. However for as much as half of people that go for this, the ache returns or persists so intensely that they want surgical procedure once more inside 5 years. “As surgeons and docs, we wish to take away lesions. However individuals’s ache persists extra usually than we prefer to report,” says Amira Quevedo, an obstetrician-gynaecologist who runs endometriosis medical trials on the College of Florida in Gainesville.
The ache skilled by individuals with endometriosis doesn’t replicate the quantity, measurement or kind of lesions current, and varies wildly between people. For some, the ache worsens throughout their interval; for others, it lasts all month lengthy. It might manifest as searing muscle spasms, or as vaginal, bowel or bladder ache that spreads throughout the pelvis and past.
Nature Outlook: Ache
This persistence of ache after the unique stimuli have subsided or been eliminated is a key function of many sorts of persistent ache. In some whole-body ache situations, comparable to fibromyalgia, there isn’t any clear trigger. One thing has tripped the ache system into overdrive, prompting a determined seek for reduction.
No less than within the case of endometriosis, that reduction is commonly present in switching diets. The meals individuals eat can quickly alter the huge assortment of microbes that reside within the gut, in flip releasing chemical substances that both drive or dampen ache. Observations that folks with persistent ache have completely different mixes of microbes of their intestine from different people have additionally given rise to the concept manipulating this intestine microbiome — by food plan or different means — would possibly assist.
That final result stays speculative, awaiting extra medical trials. And tinkering with the microbiome is unlikely to supply reduction for everybody, particularly when persistent ache turns into hardwired within the mind. However given the paucity of different choices, and the potential advantages, a microbiome-focused method is value pursuing. It might “considerably change the best way we perceive, diagnose and deal with persistent ache”, says Amir Minerbi, a doctor on the Rambam Institute for Ache Drugs in Haifa, Israel. However researchers are cautious of overstating the intestine microbiome’s analgesic talents. “We don’t wish to give false hope,” Minerbi says.
Intestine microbes and visceral ache
The connection between the intestine and persistent ache started to materialize twenty years in the past in research of irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), a persistent situation extra painful than its identify suggests. IBS is marked by visceral ache, which emanates from organs within the stomach and pelvis.
Regardless of many years of labor probing the connections between intestine micro organism and visceral ache in IBS, “it’s been a sluggish evolution” to acknowledge the intestine microbiome’s position, says stress neurobiologist John Cryan at College School Cork in Eire.
About 20 years in the past, animal research started to disclose that sure micro organism stimulate ache receptors on cells of the intestine in a way just like morphine, amongst different mechanisms. In 2008, Cryan’s crew confirmed that animals that had been careworn in youth by being separated from their moms developed a whole-body syndrome of irritation and sensitivity to visceral ache that was linked to modifications of their intestine micro organism1. “That was our first actual sturdy look” at how modifications in ache associated to modifications within the microbiome in an animal mannequin, he says.
Steadily, researchers realized not solely that the intestine’s resident micro organism might induce persistent visceral ache — and, the truth is, have been required for regular visceral ache sensation — but in addition that transplanting sure microbes from one animal to a different might relieve it. These findings have since been replicated in different varieties of ache, comparable to allodynia, a sort of extreme nerve ache stemming from very faint stimuli.
Human trials of probiotics have proven what Cryan says are “slight however important” analgesic results2 on visceral ache in IBS. Altogether, the proof means that “the microbiome is enjoying a key position in ache”, he provides. It’s even attainable that intestine micro organism affect not solely how neurons transmit ache, but in addition how these acute ache alerts flip persistent.
“It makes numerous sense,” says Jessica Maddern, a ache researcher on the South Australian Well being and Medical Analysis Institute in Adelaide, who lives with the visceral and persistent pelvic ache of endometriosis. The intestine is studded with nerves and continuously contacting the mind by the vagus nerve and spinal wire, she says, “so it stands to cause that it might change the best way you’re experiencing ache”. Food plan is already identified to have an effect on temper by the ‘intestine–mind axis’, however the finer particulars of how intestine microbiota affect ache are nonetheless being labored out.
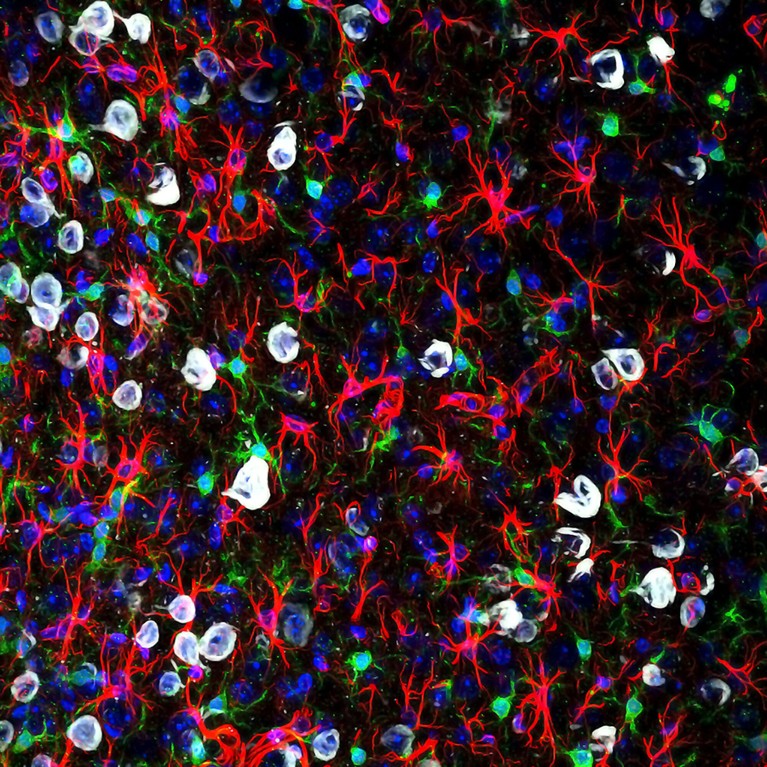
Microglia (inexperienced) can change into overly reactive and have an effect on ache alerts to the mind.Credit score: Gabriel Luna, NRI-UCSB/Wellcome/CC BY 4.0
Animal research of visceral ache have recognized particular chemical substances, produced by intestine micro organism, that may promote3 or suppress4 ache. Quick-chain fatty acids, that are produced when sure micro organism digest fibre, stimulate immune cells to launch pro-inflammatory elements, whereas bile acids suppress the exercise of sensory nerves. The consequences will be far-reaching: these metabolites can seep into the circulation by the intestine lining and cross the blood–mind barrier, altering the permeability of each buildings.
Consequently, the intestine microbiome would possibly even affect the notion of ache. Cryan says his group’s animal research present “very clearly” that mind areas identified to be concerned within the emotional and cognitive elements of ache, such because the anterior cingulate cortex, change with alterations within the intestine microbiome5. “We’re starting to see that alerts from the microbiome impinge on how visceral ache is perceived within the mind,” he says. “However we’re solely scratching the floor.”
The endometriosis window
Maddern research nerve pathways in visceral ache. Coming to this analysis some 20 years after her personal endometriosis prognosis, she was shocked at how little was identified about ache and the way to deal with it. Solely prior to now few years have researchers begun modelling visceral ache in animal fashions of endometriosis, as they do for IBS. That’s as a result of most endometriosis analysis has to this point targeted on understanding what causes the illness and the expansion of lesions, somewhat than its ache.
Nonetheless, endometriosis — which includes interconnected and overlapping ache signs — might function a window into persistent ache extra broadly. A lot-improved mouse fashions developed by Maddern and by Kelsi Dodds, a neurophysiologist at Flinders College in Adelaide, provide recent insights.
Maddern’s and Dodds’s work expands researchers’ understanding of the best way wherein ache turns into persistent, figuring out how cells within the spinal wire drive a course of known as central sensitization. In feminine mice with long-standing endometriosis, the spinal wire’s resident help cells — microglia and astrocytes — amass, change into overly reactive to and amplify ache alerts6,7. Central ache pathways change into hypersensitive to peripheral inputs, such that mild contact turns into insufferable, or persistent ache persists even with none stimuli — as is frequent after endometriosis lesions are eliminated. Different researchers modelling endometriosis in mice have equally reported swollen and subsequently activated microglia within the mind8. Activated microglia are showing in fashions of fibromyalgia, too9.
The anatomy of ache pathways additionally goes some option to explaining how the intestine microbiome might have an effect on widespread ache. Some nerve pathways innervate a number of organs within the pelvis and converge within the spinal wire, so alerts from intestine microbiota might very simply cross from the intestine over to different pelvic organs and past, Dodds says.
Meals for thought
Many ladies with endometriosis report discovering reduction by making modifications to their food plan. Some report that doing so utterly modifications their expertise of the illness, says Francesca Hearn-Yeates, who’s learning the affect of food plan on endometriosis-associated ache on the College of Edinburgh, UK.
In an as-yet unpublished survey, she requested some 2,600 individuals with endometriosis about their signs, together with bloating, cramps and ache, and what they ate. About 83% of respondents — drawn from 51 nations — stated that they had altered their diets. And of that subset of respondents, 63% stated that these dietary modifications lowered their ache. Nobody food plan stood out as the simplest, however going gluten-free and dairy-free usually helped. “It’s not a fix-all for everybody,” she says, “however the truth that it’s benefiting so many individuals is admittedly promising.”
To get at among the mechanisms concerned, she has begun an exploratory examine to profile gut-bacteria metabolites in 50 individuals with suspected endometriosis who’re awaiting diagnostic surgical procedure. A number of research have proven that folks with endometriosis have altered intestine microbiomes, but few have examined how that microbial group features as a collective10. And relating individuals’s metabolite profiles to their diets and ache, as she plans to do, is new territory. “There’s clearly this actually intricate interplay between the intestine and the mind,” she says. However the job that looms forward is to pin down how particular micro organism affect ache.
Therapeutic potential
Analysis in animals is seeking to antibiotics as a option to manipulate the intestine microbiome — and by extension, persistent ache. Two research have discovered that metronidazole, an antibiotic used to deal with gastrointestinal and reproductive tract infections, can shrink endometriosis lesions in mice11, and even cease them forming12.
This is smart: individuals with endometriosis have an abundance of anaerobic micro organism delicate to metronidazole of their intestine. Nevertheless, neither examine checked out ache. So Quevedo and her colleagues on the College of Louisville Hospital in Kentucky are investigating whether or not administering endometriosis after surgical procedure might scale back ache.
Beginning in 2020, 72 individuals with endometriosis randomly obtained both low-dose metronidazole or a placebo for 2 weeks. The 2 teams confirmed no variations in ache six weeks after surgical procedure13, however Quevedo stays optimistic. The trial runs till 2027, and contributors will report their signs six months after surgical procedure and yearly for 5 years, a timeline extra related to persistent ache.
Nevertheless, Quevedo admits that antibiotics alone may not be sufficient to quell persistent ache. They might assist to ‘reset’ the intestine microbiome by eradicating problematic micro organism. However reaching a sustained profit will most likely require probiotics — which seed the intestine with helpful micro organism — together with dietary modifications selling microbial strains linked to lowered ache.
Two small randomized trials recommend that taking every day probiotics containing chosen Lactobacillus strains can scale back painful durations in individuals with endometriosis10, however the reduction appears short-lived. This transient impact most likely displays the complexity of human ache experiences in contrast with mouse fashions, Quevedo says; after enduring endometriosis for years, most people have persistent ache that doesn’t budge.
If clinician-scientists are to search out different methods to ease ache, Quevedo says, they should differentiate between persistent ache sorts and between numerous types of endometriosis. This stratification of medical subtypes is commonly lacking from microbiome research that lump sufferers collectively, however is critical to work out which therapies alleviate whose ache. The identical is true of persistent ache usually; ache is deeply private and what eases one particular person’s discomfort would possibly do little for another person. “We all know that one therapy isn’t going to assist all people,” Quevedo says.
Fibromyalgia and past
The position of the intestine microbiome is changing into clearer in persistent ache situations that aren’t visceral in origin. The foremost instance is fibromyalgia, a ache dysfunction that typifies central sensitization — it causes widespread ache in joints, muscular tissues and tendons, and shattering fatigue, however is commonly misdiagnosed.
Minerbi’s analysis means that the intestine microbiome couldn’t solely assist to ease fibromyalgia ache, but in addition help in diagnosing it and different persistent ache situations. In 2019, his crew discovered that folks with fibromyalgia have altered intestine microbiomes, and that these slight imbalances correlated with ache and fatigue — and never with food plan, medicines or different environmental elements14. Based on Minerbi, it was the primary demonstration in people that the intestine microbiome would possibly modulate widespread, non-visceral persistent ache.
In a 2023 examine, the crew discovered that folks with fibromyalgia additionally had decrease ranges of particular bile acids of their blood in contrast with wholesome controls15. These secondary bile acids are produced by intestine micro organism that folks with fibromyalgia are inclined to lack. Actually, the decrease the extent of bile acids that they had circulating, the extra intense ache they reported — probably as a result of a few of these acids bind to neurons within the spinal wire that suppress ache. With out them, ache would possibly flare unchecked. The examine means that restoring the degrees of those bile acids might assist to scale back fibromyalgia ache.

Amir Minerbi prepares intestine microbiome samples for evaluation.Credit score: Rambam Well being Campus.
Minerbi and his crew have tried transplanting faecal matter from wholesome donors into 14 girls with fibromyalgia to handle such gut-microbiome imbalances. After 5 fortnightly remedies, 12 of the volunteers on this pilot examine, which has not been peer-reviewed, reported much less extreme ache than earlier than9. A randomized, placebo-controlled trial is subsequent.
Minerbi’s group can also be creating a machine-learning algorithm to narrate persistent ache to intestine microbiome profiles and different blood markers. To this point, the instrument differentiates solely between individuals with fibromyalgia and those that don’t have persistent ache14,15. The following step, Minerbi says, is to see “whether or not we are able to take somebody with persistent ache and say what kind of persistent ache they’ve, which is admittedly the medical query”. To that finish, researchers are investigating the intestine microbiome in numerous persistent ache situations, hoping to search out commonalities and distinct modifications between them, as one 2024 examine has carried out16.
This work has simply begun. To this point, most human research have concerned broad-stroke characterizations of the intestine microbiomes of individuals with persistent ache situations and people with out. These variations — some delicate, others hanging — implicate the intestine microbiome in a gamut of persistent situations, from inflammatory arthritic ache and migraine complications to nerve-injury ache. Whether or not these noticed variations are an underlying reason for these situations or a knock-on impact, nonetheless, stays unclear.
Hurdles forward
Most research seize solely a snapshot of the intestine microbiome. Due to this fact, Cryan says, massive, longitudinal research are wanted to trace microbiome modifications in response to signs and therapy. His analysis in animals reveals that youth stress impacts the intestine microbiome in ways in which result in persistent visceral ache in maturity, although the microbiome itself recovers17. “While you’re taking a look at ache, the microbiome will not be a mirrored image of that pathology; it is perhaps one thing that occurred manner earlier that affected ache processes,” he says.
Extra from Nature Outlooks
Nonetheless, Cryan thinks that modifying the intestine microbiota might assist to alleviate persistent ache. He cites animal research displaying that particular probiotic strains can reverse well-established ache, even when given in maturity18. That obvious plasticity presents some hope, however he says it’s important for researchers to analyze which strains of micro organism relieve persistent ache in people — and the way lengthy that impact lasts.
Regardless of these challenges, researchers are protecting an open thoughts that the intestine microbiome might assist to ease persistent ache. So immense is the burden, Maddern says, that “every part is value attempting at this level”.